Do I need full coverage insurance to finance a car? This comprehensive review examines the relationship between insurance types and car loan approval, exploring lender requirements, coverage options, and potential alternatives. Understanding these factors is crucial for securing the best possible loan terms and avoiding potential pitfalls.
Lenders assess various factors when evaluating a car loan application, including credit score, down payment amount, and the type of insurance coverage. Different types of insurance, like liability, collision, and comprehensive, have varying impacts on loan approval and interest rates. This analysis delves into the nuances of these interactions, offering a practical guide for navigating the complexities of car financing.
Understanding Loan Requirements
The auto loan landscape is riddled with complexities designed to favor lenders. Navigating these requirements demands a critical eye, as the seemingly straightforward process often conceals hidden costs and unfavorable terms. Understanding the factors lenders scrutinize is crucial to securing a fair and advantageous loan.
Factors Lenders Consider, Do i need full coverage insurance to finance a car
Lenders meticulously evaluate numerous factors when assessing car loan applications. This process is not arbitrary; it’s a calculated risk assessment. Key considerations include:
- Credit history: A significant factor, credit scores directly influence approval odds and interest rates. A strong credit history demonstrates responsible financial management, while a poor one signals potential risk.
- Debt-to-income ratio (DTI): This ratio measures the proportion of an applicant’s monthly debt obligations to their monthly income. High DTI ratios suggest a potential strain on the borrower’s ability to manage additional debt, making them less attractive to lenders.
- Down payment amount: A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, thereby lowering the lender’s risk and potentially leading to better interest rates and terms.
- Loan-to-value ratio (LTV): This ratio compares the loan amount to the vehicle’s appraised value. A lower LTV indicates less risk for the lender.
- Vehicle type and condition: The age, make, model, and condition of the vehicle significantly impact the loan amount and interest rate. More valuable or newer vehicles often command better terms.
Impact of Credit Scores
Credit scores are a crucial determinant in loan approval and interest rates. Lenders use credit scores to gauge the borrower’s creditworthiness. Lower scores translate to higher risk, leading to less favorable loan terms.
- High credit scores (e.g., 750+) typically grant access to the most favorable interest rates and loan terms. These borrowers often qualify for lower interest rates, faster approvals, and more flexible loan options.
- Medium credit scores (e.g., 650-749) often yield moderate interest rates and terms. The loan process might take slightly longer, and loan terms might be less favorable than those of high-credit-score borrowers.
- Low credit scores (e.g., below 650) often lead to significant hurdles in securing favorable loan terms. High interest rates, longer loan terms, and potential loan denial are common outcomes for borrowers in this category. Borrowers with low credit scores may need to explore alternative financing options or improve their credit standing before applying for a loan.
Role of Down Payments
Down payments directly impact loan terms and approval odds. A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, decreasing the lender’s risk.
- A higher down payment often results in a lower loan amount. This directly reduces the risk for the lender, which often leads to better interest rates and more favorable terms. It also may shorten the loan term, decreasing the overall cost of the loan.
- Conversely, a smaller down payment results in a larger loan amount, increasing the risk for the lender. This typically leads to higher interest rates, potentially longer loan terms, and more stringent loan requirements.
Financing Options
Various financing options are available, each with its own set of requirements.
- Auto loans: These are traditional loans where the borrower pays back the principal amount plus interest over a set period. Requirements typically include a credit check, debt-to-income ratio assessment, and down payment.
- Leases: A lease agreement allows the borrower to use a vehicle for a specified period. Leases generally have lower upfront costs but may have higher monthly payments compared to loans, depending on the vehicle and terms. Leases also often have restrictions on mileage and usage.
Loan Comparison Table
| Credit Score | Loan Term (years) | Interest Rate (%) | Monthly Payment ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High (750+) | 5 | 4.5 | 400 |
| Medium (650-749) | 6 | 5.5 | 450 |
| Low (<650) | 7 | 7.5 | 550 |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary based on specific loan conditions, market factors, and individual circumstances.
Insurance Coverage Types: Do I Need Full Coverage Insurance To Finance A Car
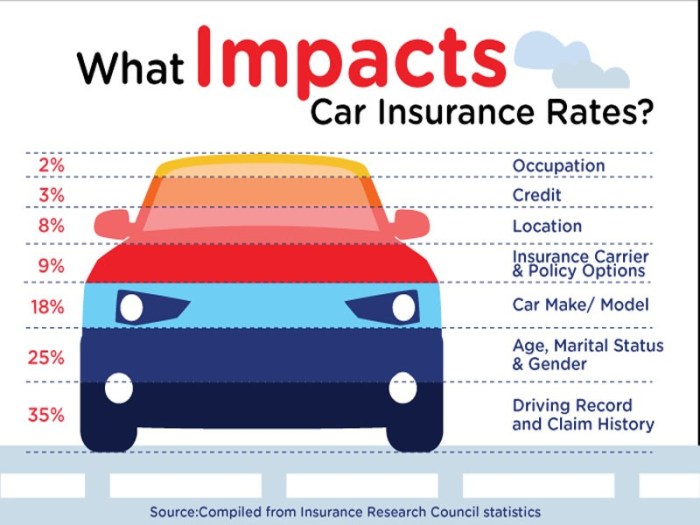
The automotive financing industry is rife with hidden costs and complexities, often designed to benefit the institutions rather than the consumer. One such area of manipulation is the requirement for various types of auto insurance. Lenders, driven by a profit motive, often leverage these requirements to increase the likelihood of repayment and minimize their own risk, irrespective of the actual need or affordability for the consumer.The differing types of car insurance coverage, from the deceptively simple liability policies to the more comprehensive packages, significantly impact the terms of a car loan.
Understanding these nuances is critical for navigating the often-complex landscape of automotive finance and avoiding potentially costly traps.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is the most basic form of auto insurance. It protects you if you are at fault in an accident, covering the other party’s damages and legal fees. It is often the minimum coverage required by law and the cheapest option, but this minimal protection offers little financial safeguard for the insured. This coverage often leaves significant financial gaps should an accident occur, and is a fundamental element in loan agreements.
Lenders frequently demand liability coverage as a baseline for approval, often viewing it as the bare minimum to prevent the loaner from being financially exposed to potential legal costs from accidents.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage protects your vehicle if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. This coverage significantly reduces the financial burden if the insured’s vehicle is damaged in an accident. Lenders frequently see collision coverage as a necessary component to protect their investment in the vehicle. Failure to obtain this coverage can make loan approval significantly more difficult.
This is due to the lender’s concern about the value of the vehicle declining if it is damaged. In the event of an accident where the insured is at fault, the lender is potentially exposed to a substantial financial loss, which is why it’s often demanded.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage goes beyond collision, protecting your vehicle against non-collision damage, such as vandalism, fire, or theft. This comprehensive protection, while seemingly beneficial, is often perceived by lenders as a luxury, rather than a necessity. The lender’s interest is primarily in securing their investment, and comprehensive coverage is viewed as an added layer of protection. The presence of this coverage is often seen as a sign of responsible financial management.
Lenders may require or prefer this coverage to mitigate their risk in cases of significant damages, especially theft or fire.
Impact on Loan Applications
Lenders often require specific types of insurance coverage to mitigate their risk. Liability coverage is usually a baseline requirement, but collision and comprehensive coverage are often preferred. The lack of adequate coverage can result in loan denial or significantly more stringent loan terms. A loan applicant without comprehensive insurance is viewed as potentially jeopardizing the lender’s investment, especially if the vehicle is significantly damaged or stolen.
This is because lenders are required to account for the risk of financial loss if the vehicle is damaged.
Insurance Coverage Comparison
| Coverage Type | Description | Impact on Loan | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liability | Covers damages to others in an accident where you are at fault. | Often a minimum requirement for loan approval. | A borrower is at fault in an accident, causing $10,000 in damages to another party. Liability insurance covers the damages. |
| Collision | Covers damage to your vehicle in an accident, regardless of fault. | Often preferred by lenders to protect their investment. | A borrower’s vehicle is damaged in a collision, regardless of who was at fault. Collision insurance covers the repairs. |
| Comprehensive | Covers damage to your vehicle from events other than collision, such as vandalism, fire, or theft. | Lenders often view it as an added layer of protection. | A borrower’s vehicle is vandalized, resulting in significant damage. Comprehensive insurance covers the repairs. |
Full Coverage and Loan Approval
The auto loan industry, often a labyrinth of opaque terms and conditions, frequently pits consumers against predatory lending practices. Full coverage insurance, often presented as a prerequisite for loan approval, is a crucial element in this power dynamic. Understanding the intricacies of this relationship is paramount for navigating the complexities of securing a car loan.The connection between full coverage insurance and loan approval is a fundamental aspect of the financing process.
Lenders view full coverage insurance as a form of protection against financial losses in case of an accident or damage to the vehicle. This security net, however, is often wielded by lenders to exert pressure on borrowers, potentially exploiting their financial vulnerability.
Full Coverage Insurance Requirements
Lenders often prioritize full coverage insurance to mitigate their risk. This protection shields them from substantial financial burdens in the event of a car accident or damage, safeguarding their investment in the loan. The lender’s position is one of self-preservation, a rational response in a business environment where risk management is paramount. However, this rationale can be exploited in a market where transparency and consumer protections are lacking.
Comparison of Insurance Coverage Types
- Comprehensive Coverage: This protects against damages not related to collisions, such as vandalism, fire, or hail. Its inclusion in a loan package often serves as a crucial safeguard for the lender, and failure to maintain this coverage can jeopardize the loan.
- Collision Coverage: This covers damages resulting from collisions with other vehicles or objects. Lenders often consider this coverage essential to secure their investment, and its absence could lead to loan denial or unfavorable interest rates.
- Liability Coverage: This only covers damages you cause to others. It is often insufficient to meet lender requirements for loan approval, signaling a higher risk to the lender.
The varying levels of insurance coverage directly affect the terms and conditions of the loan, including interest rates and loan approval. Higher levels of coverage, like full coverage, translate to lower perceived risk for the lender, which can result in more favorable interest rates. This relationship underscores the inherent power imbalance between the lender and the borrower.
Consequences of Lacking Full Coverage
Failing to maintain full coverage insurance can have serious consequences for loan approval. Lenders may reject loan applications altogether or impose significantly higher interest rates, effectively penalizing borrowers who fail to meet their minimum risk assessment criteria. This often reflects a flawed system where lenders prioritize their own financial security over the potential hardships of borrowers.
Loan Approval and Interest Rates
The level of insurance coverage directly impacts loan approval and interest rates. Full coverage, demonstrating a commitment to responsible vehicle ownership and mitigating financial risk, typically results in lower interest rates and a higher likelihood of loan approval. Conversely, inadequate coverage can result in higher interest rates and potential loan denial, further exacerbating the financial burden on the borrower.
Scenario: Full Coverage Requirement
A scenario where full coverage insurance is required for loan approval involves a high-risk vehicle model, like a luxury sports car, or a vehicle that requires a high deductible for insurance claims. Lenders in this instance are often unwilling to take on the added risk of a collision or damage without the security of full coverage insurance. This illustrates how the financial landscape of the automotive industry often disproportionately burdens consumers.
Alternatives to Full Coverage
The automotive financing industry is a battleground of conflicting interests. Lenders, driven by risk mitigation, often demand full coverage insurance as a prerequisite for loans. However, this blanket requirement can unfairly burden consumers and, in some cases, be unnecessary. This analysis explores scenarios where full coverage might not be the sole acceptable solution, examining alternatives and their implications for loan applications.The pressure to maintain full coverage insurance can be a financial burden, especially for consumers who might face significant upfront costs or may not be able to afford it.
This often leads to a complex dance between affordability and the demands of lenders.
Situations Where Full Coverage Might Be Unnecessary
A full coverage policy is often a costly requirement, particularly in regions with lower accident rates or where vehicles are older or less valuable. Lenders, in their pursuit of profit and risk mitigation, often impose a standardized requirement for full coverage. However, this standardization may not always be justified. Factors like low-accident areas, the vehicle’s age and condition, and the overall risk profile of the borrower can all contribute to the appropriateness of alternative coverage options.
Acceptable Alternatives to Full Coverage
Several insurance options can satisfy lenders’ risk requirements without the full cost of comprehensive coverage. These may include collision coverage only, or a combination of liability and comprehensive coverage. The choice often depends on factors such as the borrower’s driving record, the vehicle’s condition, and the specific loan terms. These alternative options are often more affordable and may be more appropriate for particular circumstances.
Comparing Insurance Options
A crucial step in understanding alternatives is comparing the pros and cons of different coverage types. A comprehensive table illustrating the various options is below:
| Coverage Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Full Coverage | Provides maximum protection against all types of damages. | Highest premiums, potentially unnecessary for some borrowers. |
| Collision Coverage Only | Lower premiums than full coverage. | Doesn’t cover damage from incidents like vandalism or weather events. |
| Liability-Only Coverage | Lowest premiums. | Offers minimal protection. High risk of financial loss if an accident occurs. |
| Comprehensive Coverage | Protects against damage from incidents not covered by collision, such as vandalism, theft, or natural disasters. | Still higher than liability-only, but lower than full coverage. |
Loan Application Process with Alternative Coverage
The loan application process may vary depending on the chosen alternative coverage. Lenders often have specific requirements for alternative insurance policies. Documentation and verification procedures are essential to ensure compliance with these requirements. A lender may require proof of insurance coverage, details of the policy, and a statement of any exclusions or limitations in the coverage.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Alternative Insurance
Choosing an alternative insurance type can have several implications for borrowers.
- Potential Risk 1: Higher out-of-pocket expenses in case of an accident or damage not covered by the alternative policy.
- Potential Risk 2: Rejection of the loan application if the alternative coverage does not meet the lender’s minimum requirements.
- Potential Benefit 1: Significant savings on insurance premiums, freeing up funds for other financial needs.
- Potential Benefit 2: Increased flexibility in choosing an insurance policy that best suits the borrower’s individual needs and circumstances.
Understanding Lender Requirements
The financial industry, particularly car lending, often presents a maze of regulations and requirements, often designed to minimize risk for lenders. Understanding these requirements is crucial for securing a car loan, and navigating these complexities can often feel like navigating a political minefield. Lenders, driven by their own profit motives and risk assessments, aren’t always transparent about their criteria, leaving consumers vulnerable to hidden pitfalls.
Common Lender Requirements Regarding Insurance Coverage
Lenders meticulously evaluate insurance coverage to assess the risk associated with loan defaults. A critical component of this assessment is the level of coverage and the financial stability of the insurance provider. This is often more complex than simply verifying a policy exists.
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: Lenders often mandate a specific minimum level of liability coverage, sometimes even comprehensive and collision coverage. These vary greatly depending on the lender and the perceived risk profile of the borrower.
- Insurance Provider Reputation: Lenders may scrutinize the reputation and financial strength of the insurance company providing the coverage. This is a crucial aspect of the risk assessment. A reputable insurer with a solid financial standing is more likely to be viewed favorably than an insurer with a history of financial troubles.
- Proof of Insurance: Lenders require demonstrable proof of insurance coverage. This usually involves a copy of the insurance policy or a certificate of insurance, and verification of the insurance company’s details.
- Insurance History: Some lenders will review the applicant’s insurance history for claims or lapses in coverage, further evaluating the individual’s responsibility and reliability. A history of frequent claims may signal a higher risk of future problems.
Varying Requirements Across Lenders
Different lenders have varying approaches to evaluating insurance coverage. This is not a standardized process. A lender focused on high-risk loans might have more stringent requirements than one specializing in low-risk borrowers. The lender’s own internal risk assessment model, coupled with economic conditions, plays a major role in their insurance requirements.
- Loan Type: Subprime auto loans, for instance, typically have higher insurance coverage requirements than prime loans, reflecting the greater risk associated with such loans. This is a common practice to mitigate potential losses.
- Credit Score: Lenders with stringent credit policies often link insurance requirements to the borrower’s creditworthiness. A low credit score could result in higher insurance requirements. This is a direct correlation, as lenders view a lower credit score as a greater risk.
- Vehicle Value: The value of the vehicle plays a role in determining insurance coverage requirements. A more expensive car often necessitates a higher level of coverage to protect the lender’s financial interest. Lenders want to ensure the vehicle is adequately insured in case of accidents or damage.
Determining Specific Insurance Requirements
To ascertain the precise insurance requirements from a specific lender, contacting the lender directly is essential. This is a crucial step in the loan application process, as it avoids misinterpretations or misunderstandings.
- Contact the Lender Directly: Communicating with the lender directly is paramount. They can provide the specific details of their insurance coverage requirements, which are often detailed in their loan documents. This is a direct approach that ensures accuracy and avoids ambiguity.
Handling Rejection Due to Insufficient Coverage
A lender’s rejection of an application due to insufficient insurance coverage underscores the importance of meticulous preparation. It’s a critical aspect of the loan process.
- Review Lender Requirements: Carefully examine the lender’s specific requirements to identify the gap in coverage. This step is crucial in understanding why the application was rejected.
- Adjust Insurance Coverage: If necessary, adjust insurance coverage to meet the lender’s requirements. This could involve purchasing additional coverage or adjusting the existing policy.
- Seek Alternative Financing Options: If meeting the lender’s requirements proves impossible, exploring alternative financing options is essential. It might involve seeking loans from different lenders or finding other financial solutions.
Common Lender Policies Regarding Insurance
Lenders often have established policies regarding insurance coverage. These policies vary considerably, highlighting the non-standardized nature of the car loan process.
| Lender Type | Typical Insurance Policy Requirements |
|---|---|
| Subprime Lenders | Higher minimum coverage levels, stringent checks on insurance providers, and thorough review of applicant’s insurance history. |
| Prime Lenders | Generally lower minimum coverage levels, but still verify the insurance company’s reputation and the applicant’s history. |
| Online Lenders | May have automated systems that check insurance information, and may rely on third-party verification services. |
Practical Scenarios and Illustrations
The financial landscape surrounding car loans often presents a complex interplay of factors, with insurance coverage playing a crucial role in loan approval and terms. Navigating these complexities requires a critical understanding of the motivations behind lender requirements and the potential consequences of inadequate protection. This section provides illustrative scenarios to highlight the importance of carefully considering insurance options when pursuing a car loan.
Full Coverage Insurance Recommendation
Lenders often prioritize full coverage insurance for loans due to the substantial financial risk associated with vehicle damage or theft. Full coverage insurance protects both the lender’s financial interest and the borrower’s personal assets, mitigating potential losses in case of accidents or incidents. A prime example is a high-value luxury vehicle, often requiring full coverage to compensate for potential extensive repair costs or total loss.
In such cases, the lender needs comprehensive protection to minimize financial exposure. Additionally, a borrower with a less-than-stellar credit history might find that full coverage significantly improves their chances of loan approval.
Alternative Insurance Options
Alternative insurance options might be acceptable for car loans in certain circumstances. A young driver with a pristine driving record and a low-value used car may face lower insurance premiums. In this case, comprehensive coverage might be overkill. A carefully considered comprehensive policy or comprehensive insurance might suffice. The affordability and practicality of alternative coverage options can be weighed against the risks involved, as Artikeld in the lender’s requirements.
Loan Denial Due to Insufficient Coverage
Insufficient insurance coverage can lead to a loan denial, especially for high-value vehicles or those with a history of claims. A borrower with only liability insurance and a high-value import, for instance, may be rejected by the lender. The lender’s assessment of risk, which is heavily influenced by insurance coverage, is often the deciding factor in loan approval. This is particularly true for loans secured by the vehicle, where the lender’s risk exposure is directly tied to the vehicle’s condition and the borrower’s insurance.
Determining the Best Insurance Option
Determining the best insurance option hinges on a careful analysis of personal circumstances. Factors such as the vehicle’s value, the driver’s history, the local insurance market conditions, and the lender’s requirements must be meticulously evaluated. The potential costs of insufficient coverage must be weighed against the affordability of comprehensive insurance. An honest appraisal of these variables is crucial in avoiding future financial pitfalls.
Case Study: Choosing Car Insurance
A 25-year-old recent graduate, Sarah, is purchasing a used compact car for her first commute. Her credit score is good, and she has a spotless driving record. However, her budget is tight. She explores liability insurance, which covers the other party in an accident but not her own vehicle. The lender requires full coverage, but liability insurance is significantly cheaper.
Sarah carefully assesses the value of the car and her personal risk tolerance. She consults with multiple insurance providers and compares policy options, eventually choosing a comprehensive policy that provides sufficient coverage at an affordable premium. This decision minimizes her risk and satisfies the lender’s requirements while prioritizing her financial well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the necessity of full coverage insurance for car financing depends heavily on individual circumstances and lender policies. While full coverage often strengthens loan applications, alternative options exist for borrowers who can demonstrate sufficient risk mitigation. Careful consideration of personal financial situations and lender requirements is essential to make informed decisions regarding insurance coverage when financing a vehicle.
This guide provides a framework for evaluating various insurance options and understanding lender preferences, ultimately empowering individuals to secure favorable loan terms.
Popular Questions
Does a low credit score automatically mean I can’t get a car loan?
No, a low credit score might impact loan approval and interest rates but doesn’t guarantee denial. Lenders often consider various factors beyond credit score, including down payment, income verification, and insurance coverage.
What are the potential risks of using lower coverage insurance?
Using lower coverage insurance options may increase the risk of financial loss in case of an accident or damage to the vehicle. The lender may require higher down payments or stricter loan terms to mitigate this risk.
How do different lenders have varying requirements regarding car insurance?
Lenders have varying requirements based on their risk assessments and policies. Some may require full coverage, while others might accept alternative options, or specific coverage levels. Direct communication with the lender is essential to clarify their precise requirements.
What should I do if a lender rejects my application due to insufficient insurance coverage?
If a lender rejects an application due to insufficient insurance, exploring alternative coverage options and providing additional documentation to demonstrate financial responsibility may be necessary. Contacting the lender for clarification regarding their specific requirements is crucial.
