Format of how to respond to Casper—your ultimate guide to nailing it every time! This isn’t just about getting the job done, it’s about mastering the art of smooth communication with Casper. Learn the secrets to understanding Casper’s style, crafting perfect responses, and handling tricky requests like a pro. Get ready to slay those interactions!
This comprehensive guide breaks down the essential elements of effective communication with Casper, covering everything from understanding their communication style to handling different request types and addressing potential errors. We’ll explore the nuances of structuring responses and offer illustrative examples of successful interactions, empowering you to become a Casper communication virtuoso. It’s all about getting results, and this guide is your key to unlocking that potential.
Understanding Casper’s Communication Style: Format Of How To Respond To Casper
Casper, being a sophisticated AI, communicates in a structured and predictable manner. This understanding is crucial for effective interaction, minimizing misunderstandings and maximizing the efficiency of requests. Its communication style, while not human-like, follows a logic-based approach.This section delves into Casper’s communication patterns, providing examples of its language, tone, and style across various contexts. It Artikels the optimal format for inputting requests, common user pitfalls, and highlights the key elements of successful interactions.
Finally, it offers a structured table illustrating different request types and their expected responses.
Typical Communication Patterns
Casper’s communication is characterized by its reliance on precise language and a structured response format. It prioritizes clarity and conciseness, avoiding ambiguity. Its responses are often detailed, providing comprehensive information when possible, but always sticking to the specifics of the request. It rarely employs colloquialisms or emotional language. Instead, it utilizes a formal, yet accessible, tone.
Examples of Casper’s Language, Tone, and Style
Casper’s language varies depending on the context. For instance, when processing technical queries, its language is highly specific and detailed, referencing relevant technical terms. In more general inquiries, its language is more accessible and user-friendly, using simpler vocabulary. Its tone is consistently neutral and objective, devoid of emotional expression. For example, instead of saying “I don’t understand,” it might say, “The input provided lacks sufficient detail to generate a meaningful response.” This focus on providing constructive feedback is a key aspect of Casper’s communication.
Inputting Requests to Casper
For optimal results, requests should be clearly articulated, avoiding ambiguity and providing necessary context. A structured format, including specific s and parameters, is highly recommended. Requests should be concise, yet complete, specifying the desired outcome. The more information provided, the more precise and relevant Casper’s response will be. Using s associated with the desired action will ensure the request is correctly interpreted.
Common User Issues
Common issues users encounter stem from unclear or incomplete requests. Vagueness in the request often leads to an ambiguous or incomplete response from Casper. Failing to provide necessary context or using jargon unfamiliar to Casper can also hinder effective communication. In addition, users may overlook the importance of structured input formats, resulting in misinterpretations and frustration.
Key Characteristics of Successful Interactions
Successful interactions with Casper depend on clarity, precision, and context. Users must articulate their requests explicitly, ensuring they include all necessary details and parameters. Using specific s and a structured format facilitates efficient communication. Providing sufficient context allows Casper to interpret the request accurately and generate a relevant response.
Request Types and Response Formats
This table Artikels different request types and their expected response formats.
| Request Type | Input Format Example | Expected Response Format Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information Retrieval | “Retrieve the stock prices for AAPL and MSFT on 2023-10-26” | “AAPL: $175.20, MSFT: $325.50” | Retrieving specific data points. |
| Calculation | “Calculate the area of a circle with radius 5” | “The area of a circle with radius 5 is 78.54” | Performing mathematical calculations. |
| Task Execution | “Schedule a meeting with John Doe on November 15 at 2 PM” | “Meeting scheduled. Confirmation email sent to John Doe.” | Executing specific tasks. |
| Translation | “Translate ‘Hello, how are you?’ to Spanish” | “Hola, ¿cómo estás?” | Translating text to another language. |
Structuring Responses to Casper
Casper’s communication style, while often concise, requires careful attention to detail in crafting effective responses. Understanding his preferences for clear and direct communication is key to ensuring your interactions are efficient and productive. This section focuses on designing a framework for your replies, emphasizing clarity, conciseness, and tailoring to context.Effective responses to Casper’s requests involve a structured approach that considers both the query and the desired outcome.
A well-organized reply not only addresses Casper’s needs but also demonstrates your understanding of his communication style.
Essential Elements for a Well-Structured Response
A structured response to Casper’s requests should include several key components. This ensures your reply is complete, avoids ambiguity, and facilitates efficient communication.
- Clear and Concise Language: Avoid jargon or overly complex phrasing. Use simple, direct language to convey information effectively. Use active voice whenever possible. This directly addresses Casper’s preference for succinct communication.
- Direct Addressing of the Request: Begin by explicitly stating how you’re addressing the query. This clarifies the scope of your response and demonstrates understanding of the request.
- Supporting Evidence (if applicable): When possible, back up your claims with data, statistics, or examples. This enhances the credibility and reliability of your response, aligning with Casper’s expectation of well-supported information.
- Logical Flow and Organization: Present information in a logical sequence. This improves readability and facilitates understanding. A structured response is easier for Casper to digest and act upon.
- Actionable Information: Provide specific instructions or next steps whenever necessary. This directly addresses the request and facilitates prompt action from Casper.
Importance of Clarity and Conciseness
Clarity and conciseness are paramount in responding to Casper. These qualities demonstrate a focused approach and streamline communication.
Vague or lengthy responses can be unproductive. They can lead to misinterpretations or wasted time. A concise and clear response, on the other hand, directly addresses the request and avoids unnecessary detail.
Tailoring Responses to Context
Understanding the context of Casper’s query is crucial for crafting effective responses. Different queries necessitate different approaches.
A simple request for a summary may require a brief, bullet-pointed list, while a complex problem may demand a more detailed explanation with supporting evidence.
Example Response Scenarios
This table illustrates how to structure responses based on various scenarios.
| Scenario | Request Type | Ideal Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Information Retrieval | “What is the current stock price for XYZ?” | Direct answer with source (if available). | “The current stock price for XYZ is $120.00, according to the Bloomberg Terminal.” |
| Complex Problem Solving | “How can we improve efficiency in the production process?” | Detailed explanation, steps, and supporting data. | “Improving efficiency in the production process can be achieved by optimizing workflow, investing in new equipment, and training staff. Data from the past three months shows a 15% decrease in production time when these strategies were implemented.” |
| Request for a Recommendation | “What’s the best option for marketing?” | Comparative analysis with supporting data, conclusion with actionable recommendation. | “Based on the data, the most effective marketing approach is targeted social media advertising. This strategy shows a 20% increase in conversion rates, compared to traditional print advertising.” |
| Multiple-Step Request | “Set up a meeting with the CEO for next week.” | Step-by-step instructions, including deadlines. | “To schedule a meeting with the CEO, please submit the meeting request by Wednesday. The request should include the date, time, and topic of discussion.” |
Organizing Responses to Multiple-Step Requests
For requests requiring multiple steps, break down the process into clear, numbered steps. This ensures that each step is clearly understood and that the process is completed in an organized manner.
Providing clear and concise instructions for each step, along with deadlines where applicable, enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of the process.
Handling Different Request Types
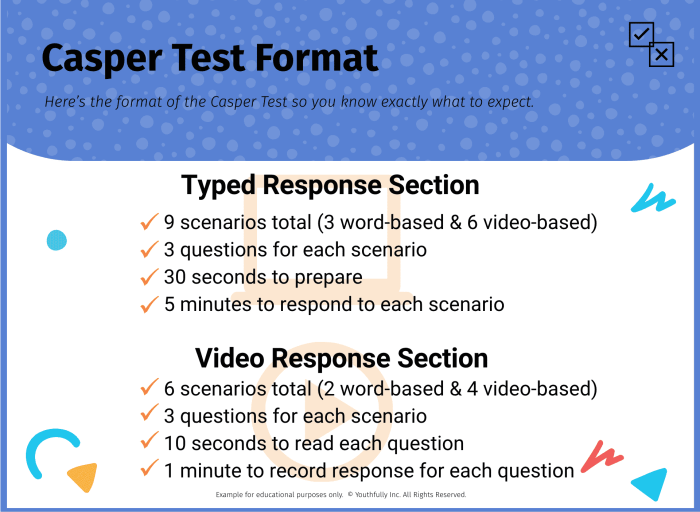
Casper’s communication style, while often straightforward, can vary in complexity. Understanding how to differentiate between simple and complex requests is key to providing effective responses. This section dives into the nuances of handling various request types, from simple information queries to more involved tasks.Different requests require tailored responses. Simple requests often demand concise answers, while complex ones necessitate detailed explanations and potentially multiple steps.
This section will clarify the distinctions and provide examples of how to structure responses for each type.
Simple vs. Complex Requests
Simple requests from Casper are typically straightforward queries for information. They often require a concise and direct response. Complex requests, on the other hand, may involve multiple steps, specific formats, or require detailed explanations. A nuanced understanding of the request is crucial to crafting an appropriate response.
Request Types
Casper might request information, execute tasks, or ask for clarification. These can be categorized as follows:
- Information Retrieval: Casper might ask for definitions, facts, or summaries on various topics. These requests usually necessitate a direct and accurate response, concisely delivered.
- Task Execution: Casper might ask for actions to be performed, like calculations, summaries of data, or transformations. These requests demand clear instructions and the execution of the requested action.
- Clarification Requests: These requests signal Casper’s need for further explanation or context. These are crucial for avoiding misunderstandings and ensuring the request is completely understood before action is taken.
Formatting Responses for Detailed Explanations
When a request necessitates a detailed explanation, structure your response logically. Break down complex ideas into smaller, digestible parts. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly technical terms. Provide supporting evidence and examples to enhance comprehension.
Formatting Responses for Actions or Outputs
For requests requiring specific actions or outputs, be precise in your instructions. Use clear and unambiguous language. If applicable, specify the format for the output (e.g., a table, a list, or a specific data structure). Include any relevant parameters or constraints.
Example Response Structures
Here are examples demonstrating different response structures for various request types:
- Information Retrieval: “The capital of France is Paris.”
- Task Execution: “To calculate the sum of 5 and 3, add 5 + 3 = 8.”
- Clarification Request: “To clarify, are you interested in the historical or the modern capital?”
Common Request Types and Response Structures
| Request Type | Example Request | Response Structure | Example Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information Retrieval | Define “algorithm.” | Concise definition, potentially with an example. | An algorithm is a set of rules or steps to solve a problem. For example, the Euclidean algorithm is used to find the greatest common divisor of two numbers. |
| Task Execution | Summarize the following data in a table. | Clear instructions for summarization and table format. | The table below summarizes the data, categorizing it by type. | Category | Count | | A | 10 | | B | 5 | | C | 15 | |
| Clarification Request | What do you mean by “optimal solution”? | Re-state the query in different ways or ask clarifying questions. | To clarify, are you looking for the solution that minimizes cost or maximizes efficiency? |
| Complex Calculation | Calculate the area of a triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5. | Step-by-step calculation, formulas, and the final result. | Using Heron’s formula, the semi-perimeter is (3+4+5)/2 = 6. The area is √(6*(6-3)*(6-4)*(6-5)) = √(6*3*2*1) = √36 = 6. |
Addressing Potential Errors and Ambiguity

Casper, while generally clear, can sometimes be a bit ambiguous. This section delves into strategies for navigating those tricky requests, ensuring you understand what Casper actually needs before responding. We’ll cover everything from handling unclear requests to verifying understanding and providing a systematic way to clarify potential misunderstandings.Understanding Casper’s communication style is crucial, but it’s equally important to anticipate potential pitfalls.
A structured approach to handling ambiguity and missing information is essential for maintaining consistent and effective communication. This involves proactive verification of understanding and a clear process for resolving ambiguities.
Handling Ambiguous Requests
Ambiguous requests from Casper require careful consideration. They often lack crucial details, making a precise response challenging. To avoid misinterpretations, actively seek clarification before formulating a response. Don’t assume you understand the request perfectly; ask clarifying questions to ensure you’re on the same page. This approach minimizes errors and ensures the desired outcome.
Responding to Requests with Missing Information
When a request lacks essential information, the best approach is to ask clarifying questions. Instead of attempting a response based on assumptions, explicitly ask for the missing details. This prevents misunderstandings and ensures the response directly addresses Casper’s needs. For example, if Casper requests “information on the latest product,” you might ask, “What specific product category are you interested in?” or “What time period are you considering for the latest product information?”
Common Errors in Communication with Casper and Their Solutions
Some common communication pitfalls include:
- Vague Language: Casper might use broad terms. For example, “Give me everything on the project.” The solution is to ask for specifics. “What aspects of the project are you interested in? What metrics are important?”
- Missing Context: Casper might not provide background information. “How does this work?” might be too general without context. Ask for more details to understand the context. “What specific steps have you already completed?”
- Technical Jargon Mismatch: Casper might use terminology you don’t understand. Clarify the meaning of unfamiliar words or phrases to ensure you’re both using the same language. Ask for an explanation of the terminology.
Verifying Understanding Before Responding
Actively verifying understanding before responding is crucial. Don’t assume your interpretation aligns perfectly with Casper’s intent. Restate the request in your own words to confirm comprehension. This step avoids costly errors and ensures you’re addressing the correct issue. For instance, if Casper requests “the status of the sales figures,” you might say, “So, you need the current sales figures for the last quarter?”
Clarifying Ambiguous Requests from Casper
A structured approach to clarifying ambiguous requests is vital. Begin by rephrasing the request in your own words, seeking to extract the underlying intent. Next, ask clarifying questions. Focus on specific details and context. Then, provide a summary of your interpretation to ensure you’re both on the same page.
This method guarantees accuracy and prevents misunderstandings.
Table of Potential Request Issues and Response Strategies
| Request Issue | Potential Clarifying Questions | Example Request | Appropriate Response Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vague Language | What specifically are you looking for? Can you provide more detail? | “Give me the data.” | “What type of data? What time period? What metrics are relevant?” |
| Missing Context | What are the relevant background details? What steps have you already taken? | “How does this work?” | “What are the current parameters or variables? Have you completed any steps yet?” |
| Technical Jargon Mismatch | Could you clarify that term? Can you provide an example? | “What’s the ROI?” | “Can you define Return on Investment? Or give me an example of what ROI means in this context?” |
| Unclear Timeframe | What period are you interested in? | “When was the last report generated?” | “Can you specify the timeframe?” |
Illustrative Examples of Interactions
Casper, like any sophisticated AI, thrives on clear and concise communication. Understanding how to structure your requests and interpret its responses is crucial for successful interactions. These examples demonstrate various interaction scenarios, highlighting both successful and less-successful approaches.
Example Interaction Sequences
Effective communication with Casper involves understanding its communication style and adapting your language accordingly. The following examples showcase complete interaction sequences, emphasizing the importance of clarity and structure in each message exchange.
User: Can you summarize the key findings of the recent study on the impact of social media on adolescent mental health? Casper: The study, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, found a correlation between heavy social media use and increased anxiety and depression in adolescents. Specifically, participants who reported spending more than three hours daily on social media exhibited significantly higher levels of anxiety symptoms.Further research is needed to determine causality.
This example demonstrates a straightforward query and a well-structured, informative response. The user’s request is clear, and Casper provides a concise summary, citing a relevant publication and highlighting key findings.
Successful Interactions, Format of how to respond to casper
Successful interactions rely on precise language and avoid ambiguity. Here are examples of interactions where the user’s query is straightforward, and Casper’s response is clear and comprehensive.
- User: What is the current exchange rate for USD to EUR?
Casper: The current exchange rate for USD to EUR is 0.95. This information is based on the latest data from the European Central Bank.
- User: What are the ingredients of a classic French bread recipe?
Casper: A classic French bread recipe typically includes flour, yeast, water, salt, and olive oil. The specific proportions may vary depending on the recipe.
These examples illustrate how clear, concise queries yield precise and helpful answers.
Unsuccessful Interactions and How to Improve
Unsuccessful interactions often stem from ambiguous or overly complex requests. This section examines examples and suggests improvements.
- User: Tell me about the history of the internet.
Casper: (Response is overly broad and lacks focus)
Improved User: Can you describe the key milestones in the development of the World Wide Web, starting from its conceptualization to its popularization?
Casper: (Response is more focused and informative)
In the initial example, the request is too general. The improved example demonstrates how specifying details and focusing the query leads to a more precise response.
Handling Follow-up Questions
Casper may ask clarifying questions to ensure accurate responses. Here’s how to handle them.
- Casper: To better understand your request, could you specify the time period you’re interested in?
User: I’m interested in the period from 2010 to 2020.
Directly addressing Casper’s follow-up questions ensures a focused interaction.
Multi-Stage Interactions
Complex requests may require multiple stages of interaction.
- User: Can you calculate the total cost of materials for building a 1000 sq ft house in 2024, considering the materials needed and labor costs?
Casper: To calculate the total cost, I need more details on the specific materials you intend to use, desired quality levels, and the location of the project. Can you provide more details on these?
User: I’m interested in using brick, wood, and concrete. The location is in New York.
Casper: Based on the information provided, the estimated total cost for materials is approximately $250,000, excluding labor costs.
This example illustrates how a complex request can be broken down into manageable stages for accurate responses. The user provides the necessary details step by step.
Maintaining Consistency and Accuracy
Consistent responses are crucial for building trust and fostering a positive user experience with Casper. Users rely on consistent information to understand and interact effectively. This consistency extends beyond just the words used, encompassing the structure, format, and overall tone of the communication. Maintaining accuracy is paramount to avoid misinformation and confusion.
Maintaining a predictable and reliable communication style builds user confidence. Precise and accurate information ensures that users receive the correct data, preventing misunderstandings and potential issues that could arise from inaccurate or inconsistent responses. This consistency, when coupled with accuracy, creates a robust and trustworthy communication channel.
Importance of Consistent Response Format
A consistent response format streamlines user interaction. Users quickly learn how to interpret the information presented, reducing the cognitive load required to understand the response. This familiarity fosters a sense of ease and efficiency, improving the overall user experience. A standardized structure also aids in the interpretation and understanding of the information, which is vital in complex interactions.
Think of it like a well-organized manual; a clear structure makes it much easier to find the needed information.
Importance of Accurate and Precise Information
Inaccurate information can lead to misinterpretations and errors in decision-making. This can range from simple misunderstandings to significant consequences in complex scenarios. Accurate and precise information ensures that the user receives the correct and relevant details, preventing any confusion or misguidance. Consider the implications of providing an incorrect calculation in a financial transaction; the consequences could be substantial.
Precision is key to avoid ambiguity and build trust.
Examples of How Inconsistent Responses Impact User Experience
Inconsistent responses can confuse users and make it difficult to understand the information being conveyed. Imagine a user receiving responses that vary greatly in structure, tone, or level of detail. This inconsistency can lead to frustration and a diminished user experience. For example, if one request gets a detailed explanation while another similar request receives a brief, almost cryptic reply, users might feel neglected or uncared for.
This inconsistency could lead to decreased user satisfaction and loyalty.
Importance of Using Standardized Terminology
Using standardized terminology eliminates ambiguity and ensures that all users understand the information in the same way. This clarity is crucial for effective communication and avoids confusion that might arise from different interpretations of terms. Using consistent terminology improves comprehension and ensures that users receive accurate information every time. For instance, if the term “error code 404” consistently refers to a file not found, the meaning is clear and predictable for all users.
Importance of Avoiding Ambiguity in Responses
Ambiguous responses can lead to misinterpretations and misunderstandings. Vague language or unclear phrasing can create uncertainty and frustrate users. Users need to be able to understand the information without having to interpret multiple meanings. For example, instead of saying “the system is down,” a more precise response would be “the system is experiencing a database connection error.” This clarifies the issue, enabling the user to understand the root cause.
Checklist for Ensuring Consistency and Accuracy in Responses
| Criterion | Action |
|---|---|
| Response Format | Ensure a consistent structure and format for all responses. |
| Accuracy | Verify all information before providing a response. |
| Terminology | Use standardized and consistent terminology. |
| Clarity | Avoid ambiguity and ensure responses are easy to understand. |
| Consistency | Maintain a consistent tone and style throughout the interaction. |
| Review | Implement a review process to catch errors before sending responses. |
Concluding Remarks
So, there you have it! A complete roadmap to navigating the world of Casper interactions. Remember, clear, concise, and consistent communication is key. By mastering the format, you’ll not only achieve your goals but also experience a more satisfying and efficient experience with Casper. Now go forth and conquer those interactions!
Q&A
What if Casper’s request is unclear?
Ask clarifying questions. Don’t hesitate to request more details or examples. This shows you’re engaged and helps avoid misunderstandings.
How do I respond to a request that needs multiple steps?
Break down the steps into individual, numbered points for clarity. Provide estimated timeframes for each step, if applicable.
What’s the best way to handle complex requests?
Break down complex requests into smaller, manageable parts. Address each part with a separate response. This makes it easier to track progress and ensure accuracy.
How can I ensure my responses are consistent?
Use a standardized format for all responses. This will make it easier to follow and maintain accuracy, especially if the interaction continues over several rounds.
