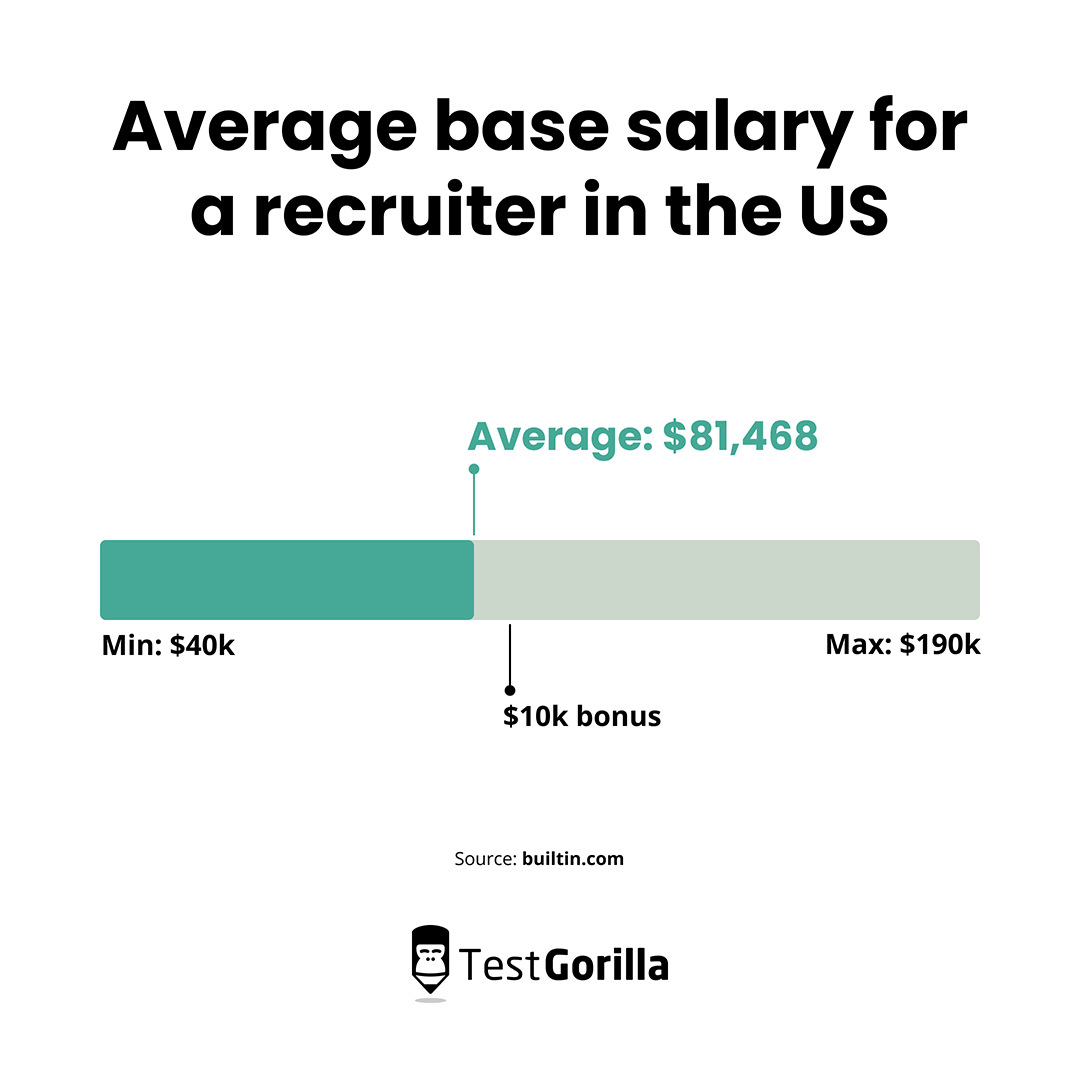
How much does it cost to hire a recruiter? It’s a question that haunts every HR and hiring manager. From agency fees to in-house salaries, the price tag can vary wildly. This guide dives deep into the murky waters of recruitment costs, comparing agency vs. in-house, and exploring the factors that determine the final bill.
Get ready to unravel the secrets behind recruitment expenses and discover how to navigate the cost landscape like a pro.
This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the hidden costs and optimizing your recruitment process. We’ll explore various recruitment models, from contingency to retainer, and show you how to calculate ROI. The ultimate goal? Hiring top talent without breaking the bank. Let’s get started!
Defining Recruitment Costs
Determining the precise cost of hiring a recruiter is multifaceted, encompassing various factors and models. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their recruitment strategies and budgets. Accurate cost estimations allow for informed decision-making and the alignment of recruitment expenses with overall business objectives.The overall cost of recruitment extends beyond the recruiter’s direct fee.
Indirect costs, such as administrative overhead, time spent by internal staff, and potential lost productivity, must also be factored into the total expense. Understanding these comprehensive costs is essential to create a realistic budget and evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of the recruitment process.
Components of Recruitment Costs
Several factors contribute to the total cost of a recruitment engagement. Direct costs are those expenses that are explicitly tied to the recruitment process, while indirect costs are those that are not directly traceable to the process. Accurate assessment of both is critical for a thorough cost analysis.
- Direct Costs: These are expenses directly associated with the recruitment process, including the recruiter’s fees, advertising costs for job postings, background checks, and any other expenses directly related to finding and assessing candidates. For example, advertising on job boards, attending industry events, or using specialized recruitment software are all direct costs.
- Indirect Costs: These are costs that are not directly tied to the recruitment process but can still impact the overall expense. These include lost productivity during the recruitment process, time spent by internal staff on recruitment tasks, and potential costs associated with failed hires (e.g., recruitment agency fees if the hiring manager cancels the recruitment process).
Recruitment Models and Their Costs
Recruitment models vary, each with distinct cost structures. Understanding these differences is critical for aligning the chosen model with organizational needs and budget constraints.
- Agency Recruitment: Using external recruitment agencies often involves paying a commission or a fixed fee based on the successful placement of a candidate. Agency fees can vary significantly based on the complexity of the role, industry, and market conditions. These costs can be predictable but may not be transparent.
- In-House Recruitment: Maintaining an internal recruitment team involves salaries, benefits, and overhead costs for recruitment staff. This model provides greater control and potentially lower costs in the long run, but it demands significant upfront investment in staffing and infrastructure.
Factors Influencing Recruiter Costs
Several factors affect the cost of a recruiter, impacting both agency and in-house models.
- Experience and Specialization: Recruiters with extensive experience and expertise in specific industries or roles typically command higher fees. A specialized recruiter for niche roles often has a greater cost compared to a generalist.
- Market Conditions: Economic factors and the demand for particular skills influence recruiter pricing. In tight labor markets, recruiter fees tend to increase as competition for talent intensifies.
- Location: Geographic location can also influence recruiter costs, with higher costs often associated with major metropolitan areas. Recruitment costs tend to be higher in areas with high competition for talent.
Typical Recruitment Service Costs
The table below provides an estimated cost range for various recruitment services. These are general estimations, and actual costs may vary depending on the specific factors Artikeld previously.
| Service Type | Description | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Search | Identifying and recruiting senior-level executives | $10,000 – $50,000+ per search |
| Technical Recruitment | Finding skilled professionals in technology fields | $500 – $5,000+ per placement |
| Entry-Level Recruitment | Recruiting recent graduates or junior professionals | $200 – $2,000+ per placement |
| Generalist Recruitment | Recruiting across various roles and industries | $300 – $3,000+ per placement |
Factors Affecting Recruiter Fees
The cost of hiring a recruiter is not a fixed amount but rather a dynamic figure influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these variables is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their recruitment strategies and avoid unnecessary expenditure. These factors range from the specific industry and geographical location to the complexity of the roles being filled and the recruitment model employed.Recruitment agencies typically structure their fees based on a variety of factors, making it important for companies to understand the variables at play to ensure they are getting a fair price for their services.
The overall cost can fluctuate significantly, so a thorough evaluation of the influencing elements is essential.
Industry Impact on Recruitment Costs
Different industries have varying recruitment needs and complexities. Specialized skills required in niche industries, such as high-tech or finance, often command higher recruiter fees compared to roles in less specialized sectors. The demand for particular skills also influences recruiter fees. High demand for specific expertise often results in a greater competition among recruiters, leading to higher rates to secure top talent.
Location Impact on Recruitment Costs
Geographic location plays a critical role in recruitment costs. Competitive recruitment markets, such as major metropolitan areas, typically attract higher fees due to the increased competition for skilled candidates. Recruiters operating in these areas often have higher overhead costs, which are then reflected in their fees. Rural or less populated areas generally present lower recruitment costs due to reduced competition.
Job Complexity and Recruitment Costs, How much does it cost to hire a recruiter
The complexity of the job opening significantly impacts recruiter fees. High-level executive searches or roles requiring specialized skills and experience often involve more extensive research, networking, and negotiations, thus justifying higher fees. Roles with simpler requirements and readily available candidates often incur lower fees. The duration of the search process also impacts the overall cost. Longer searches usually result in higher fees.
Recruitment Model Impact on Pricing
Different recruitment models employ various pricing strategies, which directly affect the overall cost. Contingency models, where recruiters are paid only if a candidate is successfully placed, can lead to variable costs, potentially impacting budgets. Retainer agreements, in which companies pay a fixed fee for a set period, offer more predictable costs. The specific terms of each model should be carefully examined.
Comparison of Different Recruitment Agency Fee Structures
| Fee Structure | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contingency | Recruiters are paid a commission upon successful placement. | Potentially lower upfront costs; risk shared with the agency. | Uncertain costs; potential for inflated fees if the agency is not efficient. |
| Retainer | Companies pay a fixed fee for a defined period of time. | Predictable costs; agency focused on long-term relationship. | Higher upfront costs; potential for agency not finding the best candidate. |
| Value-Based | Fees are based on the value delivered by the recruiter. | Alignment of interests; incentive for high-quality recruitment. | Requires careful definition of value metrics; potentially more complex to negotiate. |
Methods for Calculating Costs
Accurate calculation of recruitment costs is crucial for strategic decision-making and ensuring profitability. Understanding the various methods for determining the true cost of recruitment allows organizations to optimize their spending and maximize the return on investment (ROI). This includes factoring in both direct and indirect costs, as well as potential hidden expenses.Calculating the true cost of recruitment involves a comprehensive approach that goes beyond simply the recruiter’s fee.
This multifaceted evaluation is vital for organizations to make informed decisions regarding recruitment strategies and budget allocation. Ignoring these complexities can lead to significant inaccuracies and potentially suboptimal results.
Methods for Calculating Total Recruitment Cost
Several methods can be used to calculate the total cost of recruitment, each offering a different perspective on the overall expense. A comprehensive approach considers all aspects of the recruitment process, from initial advertisement to onboarding.
- Direct Costs: This method focuses on explicitly identifiable expenses directly related to the recruitment process. Examples include recruiter fees, advertising costs, and background check fees. By clearly delineating these costs, organizations can gain a foundational understanding of the immediate expenditure associated with a particular recruitment cycle. This approach provides a snapshot of the immediate financial outlay.
- Indirect Costs: These costs are less obvious but equally significant, representing expenses that are not directly attributable to a single recruitment effort. Lost productivity during the vacancy, administrative time spent on recruitment tasks, and potential training costs for new hires are examples. Recognizing these expenses is essential to develop a holistic understanding of the total recruitment cost.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): The TCO method extends beyond the direct and indirect costs by encompassing the long-term implications of recruitment decisions. This encompasses the cost of employee training, onboarding, and potential performance issues stemming from a poor recruitment process. It also takes into account the potential long-term savings or losses associated with hiring the right candidate.
Hidden Costs in Recruitment
Often overlooked are hidden costs that can significantly impact the overall recruitment expenditure. Identifying and quantifying these hidden costs is essential for accurate cost analysis.
- Time wasted on ineffective processes: Inefficient recruitment processes can result in lost time for hiring managers, recruiters, and candidates. This lost time translates into indirect costs and reduces the overall efficiency of the organization. For instance, a lengthy application process might deter qualified candidates or require excessive manager involvement.
- Loss of potential talent: A poorly executed recruitment campaign can lead to losing qualified candidates to competitors. This missed opportunity to attract top talent can be a substantial hidden cost, especially in competitive job markets.
- Onboarding Challenges: A new hire who isn’t a good fit for the company culture or role can result in significant onboarding challenges. This can translate into higher training costs and potential productivity losses. This highlights the importance of thorough candidate evaluation.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the ROI of recruitment spending involves a systematic approach to quantify the financial benefits generated by the recruitment process.
- Establish a clear recruitment goal: Defining specific and measurable objectives for the recruitment effort is essential. For instance, a goal might be to fill a specific position within a particular timeframe, or to reduce time-to-fill for a specific role. This provides a benchmark against which to measure success.
- Identify key performance indicators (KPIs): KPIs that measure the success of the recruitment process must be identified. These might include time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, candidate quality scores, and employee retention rates. This provides metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of the recruitment strategy.
- Measure the costs of the recruitment campaign: This involves precisely identifying all direct and indirect costs associated with the recruitment campaign. This ensures an accurate assessment of the total expenditure.
- Calculate the benefits: Evaluate the quantifiable financial gains resulting from the recruitment. This might include increased productivity, reduced turnover, or higher revenue generation from a new hire. Quantify these gains as much as possible.
- Calculate the ROI: Using the formula (Benefits – Costs) / Costs, determine the ROI. A positive ROI indicates that the recruitment investment generated a financial return.
Industry Benchmarks and Trends: How Much Does It Cost To Hire A Recruiter
Recruitment costs exhibit significant variability across industries, reflecting differing levels of complexity, required skill sets, and competitive labor markets. Understanding these benchmarks is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their recruitment strategies and budget allocation. Factors such as geographic location, economic conditions, and specific industry demands further influence these costs.
Typical Recruitment Costs Across Industries
Variability in recruitment costs is substantial across industries. Highly specialized roles, such as in technology or finance, typically command higher recruiter fees due to the intensive search and candidate vetting processes involved. Conversely, roles with readily available talent pools, such as entry-level positions in retail, might have lower associated fees. Understanding these industry-specific nuances is essential for accurate cost projections.
Recent Trends Affecting Recruiter Pricing
Several trends are influencing recruiter fees. The rise of specialized recruitment agencies catering to niche industries, such as biotech or renewable energy, has led to more tailored and potentially higher fees. The increasing use of technology in recruitment, including applicant tracking systems and AI-powered tools, has streamlined some aspects of the process, but the impact on recruiter fees remains subject to ongoing evaluation.
Impact of Market Fluctuations on Recruiter Fees
Market fluctuations directly affect recruiter fees. During periods of robust economic growth, demand for skilled labor often increases, leading to higher recruiter fees as agencies compete for talent. Conversely, during economic downturns, recruitment activity may slow, potentially resulting in lower fees. For example, in 2022, high demand for skilled labor in the tech sector led to significant increases in recruitment costs.
Geographic Variations in Recruitment Costs
Geographic location significantly impacts recruitment costs. Regions with a higher concentration of skilled labor or a more competitive job market tend to have higher recruiter fees. This is frequently observed in major metropolitan areas. Conversely, recruitment costs in less densely populated areas or emerging markets may be lower. For instance, the cost of recruiting software engineers in Silicon Valley, California, often exceeds the costs in smaller tech hubs outside of major metropolitan areas.
Comparative Analysis of Recruitment Costs
The table below presents a comparative analysis of average recruiter costs across different industries and regions, illustrating the wide range of variations. It is important to remember these are averages and actual costs can vary based on specific circumstances.
| Industry | Region | Average Recruiter Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Silicon Valley, CA | $5,000 – $15,000+ |
| Technology | Austin, TX | $3,000 – $8,000+ |
| Finance | New York City, NY | $4,000 – $12,000+ |
| Finance | Chicago, IL | $2,500 – $7,000+ |
| Healthcare | California | $2,000 – $6,000+ |
| Healthcare | Texas | $1,500 – $4,500+ |
| Retail | National Average | $500 – $2,000 |
Negotiating Recruiter Fees
Effective negotiation of recruiter fees is crucial for organizations to optimize their recruitment spend while ensuring the agency’s commitment to successful placement. A well-structured negotiation process, coupled with clear communication and a thorough understanding of the recruitment landscape, leads to mutually beneficial outcomes.
Process of Negotiating Recruitment Fees
Negotiation is a dynamic process requiring careful planning and a proactive approach. Initiating discussions early in the engagement allows for open communication and establishes a collaborative environment. This early engagement allows both parties to understand each other’s needs and expectations, paving the way for a fair and mutually acceptable agreement. Open communication, including transparent fee structures, promotes trust and a stronger partnership.
Common Negotiation Strategies
Several strategies can be employed during negotiations. A key strategy involves understanding the agency’s fee structure and identifying areas for potential reduction or adjustment. This requires a clear understanding of the services offered and the agency’s success metrics. Comparing different agencies and their fees is another effective strategy, ensuring that the chosen agency offers competitive pricing for the specific role and market.
Importance of Clear Contracts and Agreements
Clearly defined contracts and agreements are paramount to avoid misunderstandings and future disputes. These documents should explicitly Artikel the scope of work, payment terms, timelines, and termination clauses. A well-drafted contract safeguards both parties and promotes a transparent relationship, reducing the likelihood of disagreements. The inclusion of specific success metrics and performance indicators within the contract is essential.
Communicating Needs and Expectations
Effective communication is vital for a successful negotiation. This involves clearly articulating the organization’s needs, expectations, and budget constraints. This clarity ensures that the agency understands the desired outcomes and can tailor their services accordingly. Prioritizing clear and concise communication throughout the process is critical. Providing specific examples of past successful recruitment campaigns can also help illustrate the organization’s expectations and support a compelling case for negotiation.
Sample Negotiation Script for Recruiters
This script provides a framework for effective communication during negotiations.
| Scenario | Organization Representative | Recruiter |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Contact | “We’re looking for a Senior Marketing Manager with experience in digital marketing. Our budget for this role is $X, and we’re seeking candidates who meet specific criteria. Could you Artikel your fee structure and typical success metrics for similar roles?” | “Our typical fee structure is [explain clearly, specifying details like tiers, based on the candidate’s role, and the process]. For roles similar to yours, our success rate is [mention success rate] within [timeframe]. We’re confident in our ability to find a suitable candidate within your budget.” |
| Negotiation | “While your fees seem competitive, we’re aiming for a slightly lower rate of [desired rate]. We’ve seen similar agencies with comparable services for lower fees. Can we discuss a revised fee structure?” | “We understand your budget concerns. Could we discuss potential adjustments to our services, such as reducing certain components, to align with your budget? We’d be happy to explore options.” |
| Agreement | “Given the adjusted fee structure of [new fee], we are comfortable proceeding. Could we finalize the agreement with a detailed contract outlining the terms and conditions?” | “Yes, I am happy to finalize the agreement with a detailed contract including specific clauses and payment schedules.” |
Ending Remarks
So, how much does it cost to hire a recruiter? The answer isn’t straightforward, but this guide provides a comprehensive overview. We’ve explored the different components, from agency fees to in-house salaries, and highlighted the key factors influencing costs. Remember, minimizing costs without compromising quality is the key. By understanding the process, negotiating effectively, and leveraging technology, you can optimize your recruitment spend and find the perfect candidate at the right price.
FAQ Resource
What are some hidden costs associated with recruitment?
Hidden costs often include time spent by internal staff on the recruitment process, potential loss of productivity during the search, and the cost of background checks or other verification procedures.
How does the complexity of a job role affect recruiter fees?
More specialized or complex roles typically command higher recruiter fees due to the increased time and effort required to find suitable candidates. The niche expertise needed often translates to higher recruiter fees.
What are some strategies for negotiating recruiter fees?
Research the market rates, be prepared with your budget, and clearly communicate your needs and expectations. Be clear about your desired outcome and your expectations from the recruitment agency.
What are the differences between contingency and retainer recruitment models?
Contingency fees are paid only when a candidate is successfully hired, while retainer agreements provide ongoing support and are charged monthly. Contingency fees can be lower initially, but risk not getting the right people if the recruiter is not focused on the company’s needs. Retainer models offer more support and guidance but cost more upfront.
