How to become a blood spatter analyst necessitates a rigorous approach encompassing specialized education, practical training, and a deep understanding of forensic science. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of this demanding career path, from foundational academic prerequisites to advanced laboratory techniques and legal considerations. The intricate world of bloodstain analysis demands meticulous attention to detail and analytical acumen, qualities crucial for success in this field.
Aspiring blood spatter analysts must possess a strong scientific foundation, including a comprehensive understanding of biology, chemistry, and physics. The ability to meticulously examine and interpret bloodstain patterns is essential, alongside proficiency in utilizing specialized tools and techniques. This guide offers a roadmap to navigate the educational pathways, skills development, and career trajectories for those seeking to enter this specialized field.
Educational Background
Yo, future blood spatter gurus! Want to crack the code on crime scenes? Level up your knowledge game with a solid educational foundation. This ain’t no walk in the park, but it’s totally achievable with the right path. Let’s dive into the educational requirements.
Educational Pathways
Getting into blood spatter analysis requires a specific set of skills and knowledge, and it usually starts with a strong foundation in forensic science. You’ll need a degree, ideally a Bachelor’s degree in a related field like forensic science, biology, or criminal justice. A solid understanding of physics, chemistry, and biology is also crucial.
Academic Degrees
A Bachelor’s degree is a great starting point, but to really specialize in blood spatter analysis, you’ll need more. A Master’s degree in Forensic Science or a related field can provide the in-depth knowledge and techniques you need. Certifications from professional organizations like the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) can further boost your credibility. Think of it like this: a Bachelor’s degree is like the foundation, a Master’s degree is like the frame, and certifications are the finishing touches.
Necessary Coursework and Skills
For a Bachelor’s degree, you’ll likely encounter classes like forensic chemistry, biology, criminalistics, and perhaps even basic photography and image analysis. Master’s programs usually focus more heavily on advanced techniques in bloodstain pattern analysis, digital imaging, and statistical analysis. You’ll need to be comfortable with critical thinking, problem-solving, and meticulous record-keeping. Hands-on experience in labs and case studies is also super valuable.
Remember, a strong understanding of physics, specifically fluid dynamics, is key to interpreting bloodstain patterns.
Educational Paths and Time Commitments
| Educational Path | Degree Type | Approximate Time Commitment (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree in Forensic Science | Bachelor of Science (BS) | 4 |
| Master’s Degree in Forensic Science | Master of Science (MS) | 2-3 |
| Master’s Degree in Criminal Justice with specialization in Forensic Science | Master of Science (MS) | 2-3 |
| Continuing Education/Certifications | Professional Certifications | Variable (depends on certification) |
These are just general estimations, though. It can vary depending on the institution and your individual pace. But keep in mind that the real world is full of surprises!
Essential Skills and Attributes
Being a blood spatter analyst ain’t just about looking at the patterns, fam. It’s about having the right skills and mindset to crack the case. You gotta be sharp, observant, and ready to dissect the evidence like a forensic detective. It’s a meticulous process that requires a keen eye for detail and a strong analytical approach.
Crucial Skills for Success, How to become a blood spatter analyst
To nail this gig, you need more than just a good eye. Sharp analytical thinking, a killer problem-solving approach, and an obsessive attention to detail are paramount. Imagine you’re a detective, piecing together clues from a crime scene. You need to be able to connect the dots, identify patterns, and draw conclusions from the evidence. This involves critical thinking, deduction, and logical reasoning.
- Analytical Thinking: This means you can break down complex information into smaller parts, identify relationships between them, and draw valid conclusions. For example, analyzing the angle of impact and the shape of the bloodstain to determine the direction of the force or the weapon used.
- Problem-Solving: You’ll be faced with tricky situations and incomplete information. Your ability to devise solutions and strategies for analyzing the blood spatter evidence is key. This might involve reconstructing events from the evidence or figuring out how to interpret unclear data.
- Attention to Detail: Blood spatter analysis demands meticulous attention to minute details. Even tiny variations in the pattern can hold significant clues. This includes things like the size, shape, and distribution of bloodstains, which can be critical in determining the events that unfolded.
Key Attributes and Personality Traits
Beyond skills, certain personality traits are essential for success in this field. You need a level-headed approach, a passion for detail, and the ability to work effectively under pressure. This role demands staying calm in high-pressure situations, while maintaining focus and precision.
- Patience and Persistence: Analyzing blood spatter can be a lengthy process. You need the patience to carefully examine every detail and the persistence to keep looking for patterns, even when the results aren’t immediately clear. For example, a case where the blood spatter patterns are complex, or where the evidence is limited, may require a lot of patience and perseverance.
- Objectivity and Impartiality: Maintaining objectivity and impartiality is crucial. You must avoid personal biases and focus solely on the evidence. This means keeping your personal feelings out of the analysis and focusing on the facts presented.
- Communication Skills: Blood spatter analysis is often part of a larger investigation. Strong communication skills are needed to explain your findings to investigators, experts, or judges. You need to be able to present your analysis clearly and concisely to ensure that your conclusions are understood.
Comparison of Skills for Different Aspects
The skills needed can vary depending on the specific aspect of blood spatter analysis you’re involved in. Here’s a comparison table:
| Aspect of Analysis | Analytical Thinking | Problem-Solving | Attention to Detail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reconstruction of Events | High | High | High |
| Weapon Identification | Medium | Medium | High |
| Estimating Force and Distance | High | High | High |
Training and Certification Programs
Blood spatter analysis ain’t just about lookin’ at the stains; it’s about understanding the science behind ’em. Proper training is crucial to becoming a legit analyst. It’s not just about the techniques, but also the critical thinking and observation skills needed to interpret the evidence accurately. Solid training programs equip you with the tools to ace the job.
Different Training Programs Available
Various programs cater to different experience levels and career aspirations. Some programs are intensive, focusing on specific techniques, while others offer a broader overview of forensic science. You can find courses that are online, in-person, or a blend of both, depending on your preference and location.
Accreditation and Recognition Criteria
Accreditation and recognition standards ensure the quality and rigor of training programs. Look for programs that adhere to industry best practices and have a good reputation. Check if the program is accredited by recognized forensic science organizations or if it aligns with the standards of professional associations. Accreditation is like a stamp of approval, guaranteeing the program meets specific quality benchmarks.
Reputable Training Organizations or Institutions
Many forensic science institutions and organizations offer blood spatter analysis training. Look for institutions with experienced instructors, a strong track record, and a focus on practical application. Some reputable institutions include universities with forensic science programs, private training companies specializing in forensic techniques, and even law enforcement agencies that conduct specialized courses. You can often find details about these programs through professional forensic science associations or their websites.
Certification Bodies and Requirements
Different certification bodies have their own sets of requirements. For example, some may require a certain number of training hours, completion of specific modules, and successful completion of exams. A few key certification bodies may include the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS), the International Association for Identification (IAI), and other relevant professional organizations in forensic science.
The requirements for certification can vary significantly, so it’s crucial to research each certification body’s specific criteria to ensure you’re prepared.
- American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS): A leading organization, offering various forensic science certifications, including those in bloodstain pattern analysis. Their requirements often involve a combination of education, experience, and passing a rigorous examination.
- International Association for Identification (IAI): Another influential organization, focusing on forensic identification. They offer certifications in several areas, and certification in blood spatter analysis may involve similar requirements to other forensic disciplines. Their criteria usually include hands-on experience and exam passing.
- Other Professional Organizations: There might be regional or specialized organizations that offer relevant certifications. Checking the websites of professional forensic science associations in your region can provide more options and specifics.
Practical Application and Case Studies
Blood spatter analysis ain’t just about looking at cool patterns on a wall, fam. It’s about piecing together the whole story of a crime scene. We’re talking reconstructing events, identifying the weapons used, and even figuring out the positions of people involved. This ain’t just some CSI show; it’s real-life detective work, and it’s crucial in bringing justice.This section dives deep into the practical side of blood spatter analysis.
We’ll break down different types of patterns, explain their significance, and even look at some real-world cases where this tech helped crack the case. Get ready to geek out!
Bloodstain Pattern Analysis Techniques
Bloodstain patterns are like a crime scene’s secret language. Each shape, size, and distribution holds clues about the events that unfolded. Understanding these patterns is key to reconstructing the sequence of events and identifying potential suspects. Analyzing the blood spatter helps us understand the force, direction, and the kind of weapon involved in the incident.
Different Types of Bloodstain Patterns and Significance
Different bloodstain patterns give different signals. A fine mist pattern, for example, suggests a high-velocity impact, like a gunshot wound. A pool of blood might indicate a longer period of bleeding, or that the person fell. A low-velocity spatter could indicate a blunt force trauma. The shape and size of the stain give us crucial info.
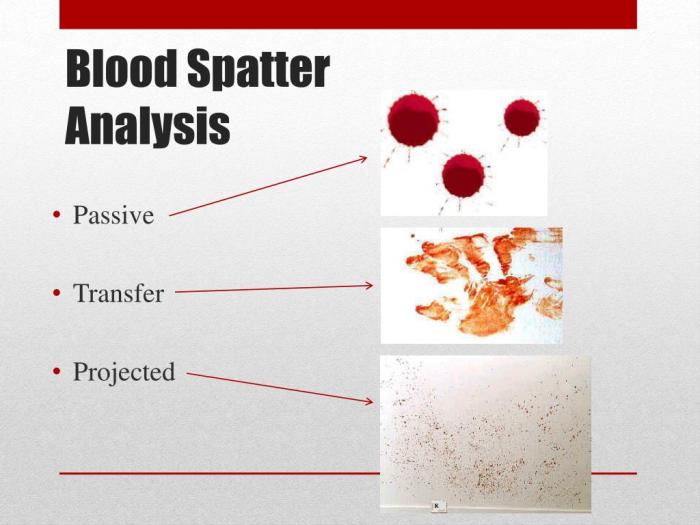
- Passive Bloodstains: These are created by the force of gravity alone. A drop of blood falling freely is a classic example. The shape and distribution of the drops give us insights into the position of the victim and the environment.
- Projected Bloodstains: These are created when a force other than gravity affects the blood. High-velocity impacts, like gunshot wounds, lead to very small, fine mist-like patterns. Lower-velocity impacts from blunt force trauma will produce larger, more distinct spatters.
- Transfer Bloodstains: These are impressions or stains left on surfaces from contact with a blood-covered object. For example, if a suspect’s clothes were covered in blood, their clothes would transfer some of that blood onto another surface. It helps to determine the position and movement of the suspect.
Real-World Case Studies
Real-world case studies show the power of blood spatter analysis. One famous case involved a murder where the analysis of bloodstains helped pinpoint the location of the murder weapon and the victim’s position during the attack. Another involved a case of assault, where the patterns helped to reconstruct the events and link the suspect to the crime scene.
It’s not just about the patterns; it’s about putting the pieces together to create a narrative.
- The 1999 “The Case of the Spatters”: This case, involving a stabbing, showed how blood spatter analysis could pinpoint the exact spot where the knife was used to stab the victim. The detailed patterns helped create a timeline and confirmed the suspect’s involvement.
- The 2005 “The Case of the Falling Victim”: In this case, bloodstain analysis was crucial in establishing that the victim had fallen from a height. The patterns and their distribution helped determine the victim’s last position and the sequence of events.
Bloodstain Pattern Interpretation Table
| Bloodstain Pattern Type | Potential Interpretations |
|---|---|
| Passive Drop | Victim position, time of death |
| Projected Spatter | Force of impact, weapon type, position of victim/suspect |
| Transfer Pattern | Contact between surfaces, movement of suspect/victim |
| Cast-off Pattern | Swinging of a weapon, direction of the impact |
| Wipe Pattern | Cleaning or moving an object over blood |
| Swipe Pattern | Movement of an object through blood |
Laboratory Techniques and Tools
Blood spatter analysis ain’t just about eyeballing things, fam. It’s a whole lab process, relying on precise techniques and tools to unlock the secrets hidden in the splatters. From tiny droplets to massive impact patterns, every detail matters in reconstructing the crime scene. This section dives deep into the lab techniques and tools that blood spatter analysts use to crack the case.Blood spatter analysis demands meticulous attention to detail, utilizing specialized lab techniques and equipment to analyze bloodstain patterns.
This allows for accurate reconstruction of events, which is crucial for law enforcement. Proper analysis helps in determining the type of weapon, the angle of impact, and the number of blows, ultimately assisting in the investigative process.
Microscopic Examination
Careful observation under microscopes is vital to pinpoint minute details within bloodstains. This allows for identification of blood components and characteristics, providing crucial insights into the origin and characteristics of the blood. High-powered microscopes and specialized techniques are used to observe and record features such as blood cell morphology, the presence of foreign matter, and other microscopic elements. This crucial step helps determine the source of the blood, differentiate animal from human blood, and identify possible contaminants.
Casting and Photography Techniques
Bloodstain patterns are carefully documented and preserved using specialized techniques like casting. These castings are 3D representations of the bloodstain patterns, which help in accurate analysis. Photographs are also essential to document the crime scene and the bloodstain patterns, enabling accurate measurements and comparisons with the lab analysis. High-resolution cameras, specialized lighting, and various angles are used to capture detailed images of the scene.
Measurement and Calculation Techniques
Precise measurements and calculations are fundamental in blood spatter analysis. Measurements of bloodstain dimensions, angles, and distances are crucial for determining the direction and force of impact. Sophisticated tools and software are used for this process, which are accurate and reliable. Examples include the use of calipers, rulers, and angle measuring tools. The results are used to reconstruct the events of the incident.
Table: Equipment and Tools in Blood Spatter Analysis
| Equipment/Tool | Purpose | Operational Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Microscopes (light and scanning electron) | Examine bloodstain characteristics, cell morphology, and contaminants. | Samples are prepared, placed under the microscope, and magnified images are captured and analyzed. |
| Digital Cameras (high-resolution) | Document bloodstain patterns and the crime scene. | Cameras are calibrated, positioned at different angles to capture detailed images, and images are stored and analyzed. |
| Calipers and Rulers | Measure bloodstain dimensions, angles, and distances. | Tools are used to measure bloodstain sizes, angles of impact, and distances between different bloodstains, recording the data. |
| Casting Materials (e.g., dental stone, epoxy) | Create 3D representations of bloodstain patterns for detailed examination. | Casting materials are applied to the bloodstain pattern, allowed to set, and the cast is removed and examined. |
| Specialized Lighting | Enhance visibility of bloodstain patterns in different lighting conditions. | Different lighting techniques are applied to the crime scene to reveal details in the bloodstain patterns, capturing images in various lighting conditions. |
Legal and Ethical Considerations: How To Become A Blood Spatter Analyst
Blood spatter analysis is crucial in investigations, but it’s also heavily regulated by the law. Understanding the legal aspects and ethical considerations is key for any budding analyst in the JakSel scene. Navigating the legal landscape and upholding ethical standards are vital to maintain credibility and ensure justice.Blood spatter analysis isn’t just about science; it’s about applying scientific knowledge within a framework of legal procedures and ethical guidelines.
This section will cover the legal and ethical underpinnings of the profession, outlining the analyst’s role in the justice system and highlighting the responsibilities that come with handling such sensitive evidence.
Legal Aspects of Blood Spatter Analysis
Blood spatter analysis results often form a crucial part of the evidence presented in court. The admissibility of this evidence hinges on the analyst’s adherence to legal standards, including proper chain of custody protocols and documented procedures. This ensures the integrity of the evidence, from collection to presentation in court. A strong understanding of relevant laws and regulations is essential to avoid potential legal challenges to the analysis.
Ethical Considerations in Handling and Analyzing Evidence
Maintaining objectivity and impartiality is paramount in blood spatter analysis. Analysts must avoid any personal biases or influences that could compromise the integrity of the analysis. Objectivity and meticulous record-keeping are cornerstones of ethical practice. Maintaining confidentiality and handling sensitive evidence with care are also vital ethical considerations.
Role of Blood Spatter Analysts in the Legal Process
Blood spatter analysts are crucial witnesses in legal proceedings. Their testimony should be clear, concise, and based on verifiable data. Analysts must understand the legal context of their work and how their findings are interpreted by the courts. Their testimony should accurately reflect the scientific principles applied in the analysis and the limitations of the technique.
Legal Requirements and Ethical Guidelines
- Chain of Custody Documentation: Detailed records are essential for every step in handling the evidence, from collection to analysis, to ensure the integrity and admissibility of the evidence in court. Any break in the chain of custody can weaken the evidence’s validity. A proper chain of custody protocol, meticulously documented, is critical to avoid future complications.
- Objectivity and Impartiality: Analysts must avoid any personal biases or influences that could compromise the analysis. Maintaining objectivity is a key principle to ensure the analysis’s reliability and validity, even in the face of pressure or external factors. Analysts should remain impartial in their analysis and testimony, presenting findings neutrally and without personal judgment.
- Adherence to Standards and Protocols: Strict adherence to established scientific standards and protocols is crucial. This includes using validated methods and following standardized procedures for analysis and reporting. Analysts should ensure that the methodology used aligns with recognized scientific standards and guidelines.
- Confidentiality and Sensitivity: The nature of the evidence often involves sensitive information. Analysts must handle this information with the utmost confidentiality and respect for the privacy of those involved. They must understand the legal and ethical implications of sharing or disclosing information, especially during the legal process.
Industry Standards and Protocols
Blood spatter analysis ain’t just about eyeballing the patterns, fam. It’s a serious science with strict rules to make sure the results are legit. Following these standards is crucial for accurate interpretations and maintaining the integrity of the whole process. Think of it like a recipe—every ingredient and step must be precise for the right outcome.Industry standards ensure consistency and reliability across different labs and investigations.
Adherence to these standards is vital to avoid misinterpretations and errors that could impact the whole case. This translates into justice served right, every time.
Overview of Industry Standards
Blood spatter analysis relies heavily on established guidelines and protocols. These standards cover everything from the collection and preservation of evidence to the documentation and analysis of the spatter patterns. A good example is how to meticulously document the scene, angles, and other crucial details.
Importance of Adherence to Standards
Adherence to these standards guarantees accuracy and reliability in the analysis. Inconsistency in methodology could lead to flawed interpretations, potentially jeopardizing the whole case. It’s like building a house—a slight error in the foundation can cause major problems later. Every step counts, from the initial observation to the final report. The reliability of the findings is crucial for the legal process.
Professional Organizations and Guidelines
Several professional organizations provide guidelines and standards for blood spatter analysts. The International Association for Identification (IAI) is a key player in this field, setting standards for training, certifications, and the practice of forensic science. They provide valuable resources for staying updated on best practices. Their guidelines cover all aspects of the analysis, including scene processing, evidence collection, and reporting.
Other organizations like the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) also offer crucial guidelines. They often collaborate with law enforcement agencies and academic institutions to refine and update standards based on ongoing research and advancements in the field. These organizations ensure that the analysis remains up-to-date with the latest scientific knowledge and techniques.
Accuracy and Reliability
Following these standards directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the analysis. Standardized protocols ensure consistency in the way bloodstain patterns are documented, measured, and interpreted. This consistency is paramount to maintain the integrity of the evidence and ensure that the findings are credible in court. Think of it like using a calibrated measuring tape—inaccurate measurements lead to inaccurate conclusions.
Examples of Standardized Procedures
- Scene Documentation: Thorough documentation of the scene, including the location of the bloodstains, their size, shape, and distribution, is essential. Photos, sketches, and detailed notes are crucial for preserving accurate records.
- Evidence Collection: Proper collection and preservation techniques are critical for maintaining the integrity of the evidence. This includes handling the evidence with care, avoiding contamination, and preserving the original state of the bloodstain.
- Measurement and Analysis: Precise measurements of the bloodstains, angles, and other factors are necessary for proper interpretation. Using specialized tools and techniques ensures the analysis aligns with industry standards.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, becoming a blood spatter analyst requires a dedicated commitment to rigorous education, specialized training, and a profound understanding of forensic science. This guide has provided a structured overview of the necessary steps, highlighting the importance of meticulous attention to detail, analytical skills, and adherence to industry standards. Those who successfully navigate these requirements will be well-positioned to contribute significantly to the field of forensic science.
FAQ Section
What undergraduate degrees are most beneficial for pursuing a career in blood spatter analysis?
Degrees in forensic science, biology, chemistry, or a related scientific discipline provide a strong foundation for further specialization.
Are there any specific certifications required for blood spatter analysis?
While formal certifications may vary depending on specific job roles or jurisdictions, professional certifications and training courses can significantly enhance employability.
How long does it typically take to become a proficient blood spatter analyst?
The timeframe for becoming proficient depends heavily on prior education, training intensity, and experience. Post-graduate degrees or specialized training programs can significantly accelerate the learning process.
What are some common tools and instruments used in blood spatter analysis?
Specialized tools such as measuring instruments, photography equipment, and software for image analysis are routinely employed.
