How to charge RV batteries effectively is crucial for maximizing the enjoyment and functionality of recreational vehicles. Proper charging methods ensure optimal battery performance, extending their lifespan and preventing costly replacements. This comprehensive guide delves into various charging techniques, from basic shore power to advanced solar and generator strategies, providing a detailed understanding of each method’s benefits and drawbacks.
This guide will cover everything from understanding different battery types and their capacities to troubleshooting common charging issues and implementing safety precautions. It also explores alternative energy sources and essential maintenance techniques to keep your RV batteries in peak condition for years to come.
Understanding RV Batteries
RV batteries are the lifeblood of your recreational vehicle, powering everything from lights and entertainment to refrigerators and appliances. Choosing the right type and size is crucial for a smooth and reliable camping experience. Proper understanding of these components ensures optimal performance and extended battery life.
Types of RV Batteries
Different battery types cater to various needs and budgets. Understanding their characteristics is essential for selecting the most suitable option for your RV. Lead-acid batteries, in particular, come in several variations, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries: AGM batteries are a popular choice for RVs due to their robust construction and ability to withstand vibrations and shocks common during travel. Their sealed design eliminates the risk of leakage, making them ideal for mobile applications. They also offer a higher resistance to sulfation, a common issue with lead-acid batteries, extending their lifespan.
- Gel Batteries: Gel batteries employ a gel electrolyte, which further reduces the risk of leakage compared to traditional flooded lead-acid batteries. They are known for their deep-cycle capabilities, making them suitable for powering appliances requiring sustained discharge, like refrigerators. However, their higher internal resistance can result in slower charging rates compared to AGM batteries.
- Lithium Batteries: Lithium batteries are rapidly gaining popularity in RVs due to their high energy density, offering more power in a smaller package. They have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance than traditional lead-acid batteries. A notable advantage is their quicker charging times, and their ability to handle multiple charge/discharge cycles without significant degradation. However, their initial cost is often higher than other types.
Capacity and Voltage
Battery capacity, measured in amp-hours (Ah), dictates how much power the battery can deliver. Higher capacity batteries can run more appliances simultaneously and for longer periods. Voltage, typically 12 volts, determines the electrical potential powering RV systems. Choosing the correct voltage is critical for compatibility with your RV’s electrical components. Battery size is directly related to the RV’s power demands.
A larger RV with numerous appliances will require a higher capacity battery.
Lifespan and Maintenance
The lifespan of RV batteries depends on several factors, including the type of battery, usage patterns, and maintenance practices. AGM batteries, for instance, typically last longer than flooded lead-acid batteries under similar conditions. Regular maintenance, including proper charging, can significantly extend the life of any battery type. Overcharging, undercharging, and extreme temperatures are common factors that contribute to shorter lifespans.
Battery Comparison Table
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Amp-Hour Rating (Ah) | Cycle Life | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGM | 12 | 100-200+ | 300-500+ | Low, sealed design |
| Gel | 12 | 100-200+ | 300-400+ | Low, sealed design |
| Lithium | 12 | 100-300+ | 2000+ | Minimal, often maintenance-free |
Note: Values in the table are approximate and can vary based on specific battery model and usage conditions.
Charging Methods
RV batteries require various charging methods depending on the available resources and desired outcome. Proper charging ensures optimal battery health and longevity. Understanding the different methods and their respective pros and cons is crucial for efficient and sustainable RV operation.
Shore Power Charging
Shore power, utilizing the electrical grid at campsites or marinas, is a common and convenient method for charging RV batteries. This method involves plugging your RV into a dedicated electrical outlet, allowing a direct current (DC) flow to the battery.
The principle behind shore power charging is straightforward. The AC power from the shore outlet is converted to DC power suitable for battery charging through an onboard inverter-charger system. This system regulates the charging current and voltage to prevent overcharging or damage to the batteries.
Advantages of shore power charging include its high efficiency, speed, and convenience. It allows for rapid battery replenishment, often at a minimal cost, making it a popular choice for frequent RV users. The convenience factor is paramount, especially for those accustomed to standard household electricity.
Disadvantages include the dependence on available shore power sources. Not all campsites or marinas offer shore power, limiting the use of this method in some locations. Furthermore, the availability of a suitable power source at the campsite is essential for this method to be functional. In certain cases, there might be limitations on the charging current, which might not be sufficient for rapidly depleting batteries.
Solar Panel Charging
Solar panel charging utilizes photovoltaic (PV) cells to convert sunlight into electricity. This electricity is then used to charge the RV batteries.
The principle behind solar charging is based on the photovoltaic effect. Sunlight excites electrons in the PV cells, creating an electric current. This current is then directed to charge the RV batteries, making it a sustainable and environmentally friendly option.
Advantages of solar panel charging include its sustainable nature, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and its independence from external power sources. The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly, making it a more affordable option compared to previous years. The reduced dependence on external power sources is a significant advantage, especially in remote areas where shore power might not be readily available.
Disadvantages of solar panel charging include the dependence on sunlight availability. Cloudy days or periods of low sunlight significantly reduce the charging capacity. Solar panels are not a fast-charging solution; charging times can be prolonged compared to other methods. The initial investment in solar panels can be substantial.
Generator Charging
Generator charging utilizes a portable generator to convert fuel energy into electricity, which then charges the RV batteries.
The principle behind generator charging is based on the conversion of mechanical energy (from the generator) into electrical energy, which is then used to charge the RV batteries. The generator’s engine runs, producing electricity to charge the batteries.
Advantages of generator charging include its ability to provide a reliable power source even in locations without shore power or sunlight. This independence from external power sources is vital in remote areas. It is a viable backup solution for charging batteries in cases of limited or unavailable alternative methods.
Disadvantages of generator charging include the need for fuel, making it less environmentally friendly than other options. Noise pollution is another consideration, especially in quiet camping environments. The cost of fuel and maintenance for the generator should be factored into the decision-making process.
Charging Method Comparison
| Charging Method | Cost | Convenience | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shore Power | Low (minimal or no additional cost) | High | Low |
| Solar Panels | Medium (initial investment) | Medium | High (reduced reliance on fossil fuels) |
| Generator | Medium (fuel cost) | Medium | High (fuel consumption) |
Maintaining Charge: How To Charge Rv Batteries
Maintaining a consistent charge is crucial for the longevity and optimal performance of RV batteries. Proper charging and maintenance practices prevent premature aging, reduce the risk of failure, and ensure reliable power when you need it most. Consistent charge levels also extend the overall life of the battery system.Consistent charging, coupled with regular maintenance, significantly improves the battery’s lifespan.
This proactive approach safeguards against costly replacements and ensures uninterrupted power access during your travels.
Importance of Consistent Charging
Consistent charging is essential for maintaining a healthy state of charge in RV batteries. Fluctuations in charge levels, whether due to deep discharges or inadequate charging, accelerate battery degradation. Maintaining a consistent charge minimizes sulfation, a chemical process that can permanently damage the battery plates, leading to reduced capacity and eventual failure. This consistent charge also ensures optimal performance for your RV’s electrical systems, guaranteeing reliable power for everything from lighting to appliances.
Checking Battery State of Charge
Regularly checking the battery’s state of charge is a vital preventative measure. A hydrometer, a tool that measures the specific gravity of the electrolyte, provides a precise indication of the battery’s charge level. Lower specific gravity often indicates a depleted state of charge, while high specific gravity suggests overcharging. A digital multimeter can also measure voltage, though this method is less precise than a hydrometer for determining the true state of charge.
Accurate measurement helps in determining whether the battery needs a recharge or if there are underlying issues requiring further investigation.
Identifying and Addressing Depleted or Failing Batteries
Signs of a depleted or failing battery include reduced cranking power, slow charging times, or a visible deterioration of the battery case. If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to address the issue promptly. A depleted battery might require a complete recharge, while a failing battery might need replacement. Consult a qualified RV technician for a comprehensive assessment to diagnose the problem accurately.
Preventing Overcharging and Deep Discharging
Overcharging can lead to overheating and damage to the battery’s internal components, while deep discharging can result in irreversible sulfation and permanent capacity loss. Overcharging can also lead to gas evolution, which can cause damage to the battery’s terminals and electrolyte. Using a battery charger with appropriate voltage and amperage settings is crucial to avoid these issues. Monitoring the battery’s charging and discharging cycles and using appropriate cutoff points will prevent such damage.
Preventative Maintenance Tasks
A proactive approach to battery maintenance significantly extends its lifespan.
- Regularly inspect battery terminals for corrosion and clean them as needed. Corrosion reduces conductivity, hindering proper charging and discharging. This preventive measure ensures efficient current flow, thereby extending the battery’s lifespan.
- Maintain appropriate ventilation around the battery. Proper ventilation helps prevent overheating and gas buildup, which can both cause damage to the battery and create safety hazards.
- Avoid leaving the RV’s electrical system in a fully discharged state for extended periods. This reduces the risk of sulfation, a chemical reaction that can lead to permanent damage and loss of capacity.
- Use a battery monitor to track charging and discharging cycles and maintain appropriate cutoff points to prevent overcharging or deep discharging. This data-driven approach allows you to monitor the battery’s health and adjust charging and discharging practices accordingly.
- Store the RV battery in a cool, dry place when not in use. Extreme temperatures can negatively impact battery performance and lifespan. Storage conditions play a significant role in the longevity of the battery.
Troubleshooting Charging Issues
RV battery charging problems can be frustrating, but understanding the potential causes and troubleshooting steps can save you time and money. A thorough understanding of your system’s components and their interdependencies is crucial for effective diagnostics. Common issues range from slow charging to complete failure, often stemming from easily identifiable problems.Identifying the root cause of charging issues is essential for effective repairs.
Proper troubleshooting involves systematically checking various components and connections within the charging circuit. This methodical approach allows you to isolate the specific problem and implement the appropriate solution.
Common Charging Problems
A well-maintained charging system is crucial for RV battery longevity. Recognizing and addressing potential problems early can prevent significant issues. Common charging problems include slow charging, no charging, and overcharging.
Slow Charging
Slow charging can stem from various factors. A crucial first step is confirming that the charging system is receiving adequate power. A low input voltage to the regulator or an insufficient charging current can result in slow charging. Additionally, faulty wiring or loose connections can impede current flow, leading to reduced charging rates.
No Charging
The absence of charging suggests a more serious problem, often requiring more in-depth investigation. A malfunctioning charger, damaged wiring, or faulty connections in the charging circuit can lead to this issue. The charging system’s voltage regulator might also be malfunctioning. A faulty or improperly wired charging system is a primary cause of no charging.
Overcharging
Overcharging can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan. Overcharging occurs when the charging system continues to supply current to the battery beyond its full capacity. An improperly adjusted regulator or a defective charging system are common causes. If the charging system is not correctly calibrated, overcharging can occur.
Troubleshooting Steps for Charging Issues
Effective troubleshooting requires a systematic approach. It involves checking various components and connections within the charging circuit. This systematic approach allows for precise identification of the problem.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Possible Causes | Troubleshooting Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Charging | Low input voltage, insufficient charging current, faulty wiring, loose connections, or a malfunctioning voltage regulator. | Check the input voltage to the regulator, ensure sufficient charging current, inspect wiring for damage or loose connections, and test the voltage regulator for proper operation. |
| No Charging | Malfunctioning charger, damaged wiring, faulty connections, or a malfunctioning voltage regulator. | Test the charger for proper operation, check wiring for damage or loose connections, inspect the connections in the charging circuit, and test the voltage regulator. |
| Overcharging | Improperly adjusted regulator, defective charging system. | Adjust the regulator settings to the appropriate level, check the charging system for any defects, and if necessary, replace the regulator or the entire charging system. |
Safety Precautions
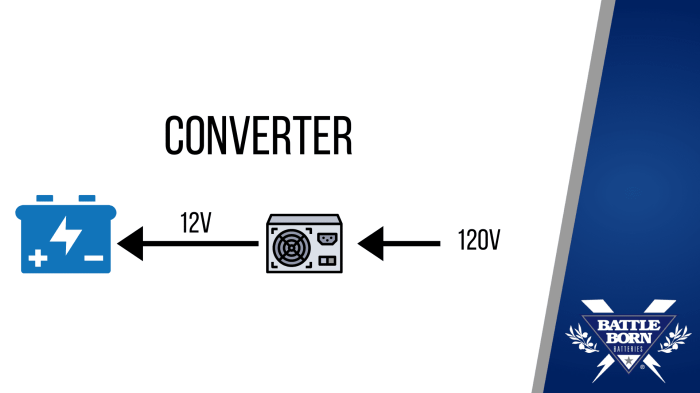
Working with RV batteries requires careful attention to safety procedures to prevent accidents and injuries. Improper handling can lead to serious hazards, including burns, acid splashes, and electrical shocks. Understanding and adhering to safety precautions is paramount for a safe and efficient RV experience.Proper handling and charging techniques, along with the use of appropriate safety gear and procedures, are crucial for maintaining a safe environment when dealing with RV batteries.
Failing to prioritize safety can lead to substantial damage and injury.
Handling Procedures
RV batteries contain sulfuric acid, a corrosive substance. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and a long-sleeved shirt. Avoid skin contact with the battery acid. If contact occurs, immediately flush the affected area with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
Electrical Safety
RV batteries store significant electrical energy. Never attempt to work on a battery while it is connected to the RV’s electrical system. Disconnect the battery terminals before performing any maintenance or troubleshooting. Use insulated tools and ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
Grounding and Insulation
Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical shocks. Ensure all electrical components are properly grounded and insulated. A faulty ground can cause dangerous voltage spikes and damage to the electrical system. Improper grounding can also lead to electrical fires. Inspect and maintain grounding connections regularly.
Potential Hazards of Improper Charging or Handling
Improper charging can damage the battery, leading to overheating, gas buildup, or even explosions. Overcharging can significantly shorten the battery’s lifespan. Never leave a battery unattended during charging, and always use a properly rated charger for the specific battery type. Incorrect handling methods, such as dropping or shorting the battery, can also cause severe damage. A battery short circuit can cause a fire or significant damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Safety Tips for Working with RV Batteries
- Always disconnect the negative (-) terminal first, then the positive (+), to avoid accidental short circuits. This is critical to prevent unexpected electrical discharges.
- Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks. Ensure that all tools are designed to withstand the electrical environment.
- Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and long sleeves. This will protect you from the corrosive nature of the battery acid.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling potentially harmful fumes. Battery fumes can be toxic.
- Inspect battery connections regularly for corrosion and ensure they are clean and tight. Regular inspections can prevent potential hazards and improve battery performance.
- Never attempt to charge a damaged or cracked battery. This can lead to unpredictable behavior and potential safety hazards.
- Never mix different battery types or attempt to charge batteries that are not compatible. Incompatible batteries can cause overheating and potential explosions.
- If you are unsure about any aspect of battery maintenance, consult a qualified RV technician. Seeking professional help is always a safe option.
Emergency Procedures
In case of an acid spill or other chemical exposure, immediately flush the affected area with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek immediate medical attention. If a fire occurs, evacuate the area and call the fire department. If electrical shock occurs, disconnect the power source immediately and call for medical assistance.
Advanced Charging Strategies
Optimizing RV battery performance goes beyond basic charging. Advanced techniques, like equalization and float charging, can significantly extend battery life and improve overall system reliability. Understanding when and how to implement these strategies is crucial for maximizing your investment and ensuring your RV’s electrical system functions seamlessly.Advanced charging strategies are not just about getting the battery fully charged; they’re about maintaining its health and longevity.
These methods address specific aspects of battery chemistry and electrical behavior, enabling you to push the performance envelope and prevent premature degradation. Implementing these strategies requires a good understanding of your battery type, your charging system, and the specific environmental conditions you’ll be facing.
Equalization Charges
Equalization charges are designed to balance the charge levels across all the battery cells. This is particularly important for batteries with multiple cells. Over time, minor variations in charge can occur, leading to potential issues like unequal expansion or contraction within the cells.Equalization charges are typically performed on a schedule. The process involves a higher-than-normal charging current for a specific duration.
This helps to distribute the charge more evenly, preventing the overcharging of some cells while others remain undercharged.
Float Charging
Float charging is a method of maintaining a constant, low-level charge on the batteries. This is ideal for situations where the batteries are not being used continuously, such as when parked for extended periods.After a battery reaches its full charge, the charging current is reduced to a trickle charge. This ensures that the battery remains topped up without the risk of overcharging, preserving the battery’s lifespan.
The float voltage is usually slightly below the full charge voltage, ensuring a consistent and gentle charge.
Implementing Advanced Strategies
The decision to use equalization or float charging depends heavily on the specific needs of your RV and its battery configuration. Consult your RV’s owner’s manual and the specifications of your battery bank to determine the appropriate charging protocols.Equalization charges should generally be performed on a schedule, typically once a month or less frequently, depending on the usage pattern and battery type.
Float charging is essential when the RV is parked for extended periods. This will help to prevent sulfation and maintain the battery’s health.
Equipment Needed
Implementing these advanced strategies requires specialized equipment. This equipment is essential for accurate and safe charging practices. A quality battery charger with adjustable settings is crucial.The specific equipment needed may include a dedicated battery charger with equalization and float charging capabilities, along with appropriate safety equipment like circuit breakers and fuses. An ammeter and voltmeter are essential for monitoring the charging process and ensuring safe operation.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific battery charger and battery system.
Battery Monitoring and Maintenance

Regular monitoring and maintenance of your RV batteries are crucial for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and preventing costly repairs. Proper care can significantly extend the lifespan of your batteries and reduce the frequency of charging issues. Ignoring these aspects can lead to premature battery failure, requiring costly replacements.Understanding your batteries’ state of charge and identifying any potential problems early on is paramount.
By consistently monitoring voltage, amperage, and state of charge, you can proactively address any emerging issues before they escalate. This proactive approach is key to maintaining a reliable and efficient RV power system.
Importance of Regular Monitoring, How to charge rv batteries
Consistent monitoring of battery health and performance is vital for preventing unexpected issues. Early detection of problems allows for timely intervention, avoiding costly replacements and extended downtime. It’s like having a health check for your RV’s power system. Regular monitoring enables you to identify subtle changes in voltage or amperage, which could indicate underlying issues that may escalate quickly if left unchecked.
Using a Battery Monitor
A battery monitor is an essential tool for tracking critical battery parameters. It allows you to precisely measure voltage, amperage, and state of charge, providing real-time data for informed decisions. This data allows you to adjust charging strategies and identify potential problems. By observing these metrics, you can understand the battery’s health and performance and make adjustments to your charging schedule and maintenance routine.
Tools and Equipment for Battery Maintenance
A comprehensive toolkit for RV battery maintenance is essential. This includes various tools for ensuring safe and effective handling. The necessary equipment includes a battery hydrometer, a voltmeter, and a multimeter for precise readings. A set of screwdrivers, including flathead and Phillips head, is also crucial for accessing and working on battery terminals and connections. A battery terminal cleaner and lubricant will maintain optimal electrical contact.
Visual Inspection of Battery and Connections
A thorough visual inspection of the battery and its connections is a crucial preventative measure. Regularly inspect the battery for any signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks. Inspect the battery terminals for corrosion, which can impede the flow of electricity. Clean any corrosion with a battery terminal cleaner, and ensure tight connections using appropriate tools. This simple inspection can reveal issues before they cause significant problems.
Pay close attention to the battery’s overall condition, looking for bulging or leaking cells. If you notice any of these signs, consult a professional immediately.
Alternative Energy Sources
Beyond traditional charging methods, RV owners are increasingly exploring alternative energy sources to power their batteries. These sources offer unique advantages, though they also come with their own set of considerations. Factors like installation complexity, cost, and environmental impact play a crucial role in determining the suitability of each option.
Wind Turbines
Wind turbines offer a potentially sustainable and renewable energy source for RV batteries. Their effectiveness depends heavily on consistent wind speeds. Areas with reliable wind patterns are ideal locations for utilizing wind turbines. A properly sized wind turbine can supplement or even replace traditional charging methods in suitable environments.
- Pros: Wind power is a clean and renewable energy source. It can significantly reduce reliance on grid power or fossil fuels. The long-term cost of operation can be lower compared to traditional fuel-based systems, especially in areas with high wind speeds.
- Cons: Installation can be complex and expensive. The efficiency of a wind turbine depends heavily on wind speed and consistency. Wind conditions can be unpredictable, leading to periods of reduced or no power generation. Wind turbines often require significant space for installation and may be visually intrusive. The initial investment cost is substantial.
Fuel Cells
Fuel cells provide a potentially clean and efficient alternative to traditional energy sources. They produce electricity by reacting hydrogen with oxygen. The generated electricity is direct current (DC), which is a more convenient form for many RV battery systems.
- Pros: Fuel cells can offer a high level of efficiency, potentially exceeding traditional methods. The emission levels are low, producing primarily water vapor. Fuel cell systems can be designed for quieter operation compared to combustion engines.
- Cons: The initial cost of fuel cell systems can be substantial. The availability of hydrogen fueling stations is currently limited, which can be a significant constraint. Storage of hydrogen gas requires specialized equipment, and potential safety concerns need to be addressed.
Comparison of Alternative Energy Sources
| Energy Source | Cost | Environmental Impact | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Turbines | High (initial investment) | Low (renewable source) | Moderate to High (dependent on wind conditions) |
| Fuel Cells | High (initial investment) | Very Low (low emissions) | High (potential for high efficiency) |
| Solar Panels | Moderate (depending on size and efficiency) | Low (renewable source) | Moderate (dependent on sunlight) |
“The choice of alternative energy source depends on factors like local weather conditions, budget, and environmental priorities.”
Final Review
In conclusion, mastering the art of charging RV batteries involves a deep understanding of battery types, charging methods, and crucial maintenance procedures. By following the detailed guidelines and troubleshooting tips Artikeld in this guide, RV owners can ensure the longevity and reliable performance of their batteries. Ultimately, this knowledge translates to a more enjoyable and hassle-free RV experience.
FAQ Insights
What are the different types of RV batteries?
Common RV battery types include AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat), Gel, and Lithium. Each type has varying characteristics in terms of capacity, voltage, lifespan, and maintenance requirements.
How do I check the state of charge of my RV battery?
A battery hydrometer or multimeter can be used to measure the specific gravity or voltage of the battery, providing an indication of its state of charge. Consult your battery’s manual for specific instructions.
What are some common charging problems with RV batteries?
Common problems include slow charging, no charging, and overcharging. Potential causes range from faulty charging systems to loose connections or low voltage.
What safety precautions should I take when working with RV batteries?
Always disconnect the battery from the system before performing any maintenance or troubleshooting. Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection. Ensure proper grounding and insulation to prevent electrical hazards.
