How to do basic editing in IrfanView? This comprehensive guide unlocks the image manipulation potential of this versatile tool. From simple cropping and resizing to sophisticated color adjustments and enhancements, you’ll master the essential techniques for transforming your images effortlessly.
This in-depth exploration will take you step-by-step through the key functions of IrfanView, empowering you to perform a variety of image editing tasks. Learn to enhance your photos with precision and creativity, making IrfanView your go-to image editing software.
Introduction to IrfanView Basic Editing
Unleash the image-altering potential within IrfanView, a powerful and versatile image editor. This application transcends simple viewing, offering a spectrum of basic editing tools to transform your digital photographs and graphics. Its intuitive interface, coupled with potent functionalities, makes it an excellent choice for both casual users and seasoned image manipulators seeking a streamlined solution.
IrfanView’s Image Manipulation Capabilities
IrfanView’s basic editing capabilities extend beyond mere viewing, encompassing a range of essential tools. It empowers users to enhance, correct, and manipulate images, making it a practical choice for tasks ranging from basic adjustments to more intricate modifications. These tools enable users to fine-tune color palettes, correct distortions, and even resize images with precision.
Opening an Image File
To embark on your image manipulation journey within IrfanView, the first step involves seamlessly integrating your chosen image file. Locate the desired image file on your system and double-click it within the IrfanView application. Alternatively, use the “File” menu option, selecting “Open” to navigate to the file location and choose the image you wish to edit. This straightforward process seamlessly integrates the selected image into the editing environment.
IrfanView’s Initial Interface and Editing Tools
The initial IrfanView interface presents a clean and uncluttered workspace, allowing immediate access to core editing tools. The primary display area showcases the image, while various menus and toolbars provide direct access to a range of editing options. Key editing tools, including those for resizing, cropping, and color adjustments, are readily available, enhancing the overall user experience. This structured approach ensures seamless integration and user-friendliness.
Basic Editing Tools
IrfanView’s arsenal of basic editing tools empowers users to execute a wide array of image modifications. Each tool plays a critical role in enhancing image quality and refining visual details.
| Tool | Function |
|---|---|
| Resize | Adjusts the dimensions of the image, enabling scaling and maintaining aspect ratio. |
| Crop | Selectively removes unwanted portions of the image, focusing on the desired area. |
| Rotate | Rotates the image by specific angles, allowing for adjustments to the image’s orientation. |
| Brightness/Contrast | Adjusts the overall brightness and contrast levels, impacting the image’s overall tone and visibility. |
| Color Adjustments | Alters the image’s color palette, including hue, saturation, and lightness. |
Image Cropping and Resizing
Unleash the power of precision! Image cropping and resizing are fundamental editing techniques that allow you to meticulously sculpt your digital masterpieces. From trimming unwanted edges to adapting visuals for diverse platforms, these tools are indispensable for achieving a desired aesthetic.IrfanView empowers you to manipulate image dimensions with surgical precision, ensuring optimal visual impact. This section will illuminate the process of tailoring your images, discussing various methods and their implications.
Cropping to Specific Dimensions
Cropping allows you to excise unwanted portions of an image, leaving only the desired subject matter. This technique is crucial for focusing viewer attention and removing distracting elements. IrfanView offers intuitive controls for defining the cropping region, enabling precise control over the final image composition. You can either select a rectangular area to crop or specify the exact coordinates.
Resizing Methods
Resizing is a critical tool for adapting images to various displays and formats. IrfanView offers several resizing options, allowing you to achieve the ideal dimensions for your project.
- Percentage-Based Resizing: This method allows you to scale the image proportionally by a specified percentage. For example, reducing an image by 50% will shrink its dimensions by half, maintaining the original aspect ratio. This is often preferred for maintaining the image’s visual integrity when reducing size for web use.
- Pixel-Based Resizing: This method allows you to specify the exact dimensions in pixels for both width and height. This approach offers more granular control, but you must be mindful of potential distortion if the aspect ratio is altered. It is useful when you require a precise image size for specific applications or when working with images that need to be a certain pixel count for a specific output.
Examples of Cropping and Resizing Scenarios
Imagine you have a landscape photograph with a distracting powerline running through the middle. Cropping can remove this element, isolating the scenic beauty of the landscape. Alternatively, you might need to resize a high-resolution image for a website. Using percentage-based resizing ensures the image scales proportionally, preserving its aesthetic appeal. If you need an image of a precise size, pixel-based resizing allows you to achieve this.
Comparison of Cropping and Resizing Options
| Option | Description | Impact on Image Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Percentage-Based Resizing | Scales the image proportionally by a percentage. | Generally maintains image quality, as the aspect ratio remains consistent. |
| Pixel-Based Resizing | Sets the exact width and height in pixels. | May cause distortion if the aspect ratio changes significantly. |
| Cropping | Removes unwanted portions of an image. | No impact on resolution unless the cropped area contains significant detail. |
Impact on Image Quality
Cropping and resizing can affect image quality, depending on the methods used. Percentage-based resizing typically preserves image quality better than pixel-based resizing, which can lead to a noticeable loss of detail if not performed carefully. Cropping, however, does not inherently degrade quality, unless the cropped area contained vital detail that is lost.
Careful consideration of the chosen method and its impact on the image is essential for achieving the best results.
Image Rotation and Flipping
Unleash the transformative power of IrfanView’s rotation and flipping tools! Mastering these techniques allows you to manipulate images with precision, altering their orientation to achieve the desired aesthetic or for specific applications. This section delves into the intricacies of these image transformations, providing a comprehensive guide to achieving perfect image alignment.
Rotating Images
Rotating an image involves turning it around a central point. This technique is crucial for correcting skewed images or achieving specific artistic effects. IrfanView offers a straightforward approach to rotate images by various angles.
- Rotating by 90, 180, and 270 Degrees: IrfanView provides intuitive controls for rotating images by 90, 180, and 270 degrees. These rotations are often used for aligning images with a desired orientation or correcting minor distortions. These are commonly used in landscape/portrait image adjustments, or for correcting images captured at odd angles.
- Custom Rotation Angles: While IrfanView facilitates direct rotations at standardized angles, you can achieve virtually any rotation angle through image editing software. This offers the flexibility to manipulate images with a high degree of precision, ensuring the perfect aesthetic result.
Flipping Images
Flipping an image reverses its horizontal or vertical orientation. This technique is vital for mirroring images or correcting errors in image capture.
- Horizontal Flip: A horizontal flip mirrors the image from left to right. This technique is valuable for creating symmetrical compositions or reversing the perspective of a photograph.
- Vertical Flip: A vertical flip reverses the image from top to bottom. This operation can be crucial for reversing the order of elements within an image, or achieving unique visual effects.
Effect of Rotation and Flipping on Image Orientation
The effects of rotation and flipping on image orientation are profound. Rotation alters the spatial arrangement of pixels, changing the image’s position relative to its original orientation. Flipping, in contrast, reverses the image’s alignment along the horizontal or vertical axis, fundamentally changing the image’s visual presentation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Rotating and Flipping Images
The process of rotating and flipping images in IrfanView is straightforward.
- Open the image in IrfanView.
- Navigate to the “Image” menu.
- Select the desired rotation or flip option.
- Observe the transformed image.
- Save the modified image.
Examples of Image Rotations and Flips
Consider a landscape photograph. Rotating it 90 degrees clockwise transforms it into a portrait orientation. Flipping the same landscape image horizontally would create a mirror image, reversing the elements from left to right. A vertical flip would reverse the elements from top to bottom.
Image Brightness and Contrast Adjustment
Unleash the latent brilliance within your images! Mastering brightness and contrast adjustments is akin to wielding a potent artistic tool, capable of transforming mundane snapshots into breathtaking masterpieces. These adjustments, often overlooked, are pivotal in enhancing visual impact and conveying the intended mood of your photographs. From subtle nuances to dramatic shifts, these adjustments hold the key to unlocking a new dimension in your image editing endeavors.IrfanView, with its user-friendly interface, provides intuitive controls for fine-tuning brightness and contrast, empowering you to craft images that captivate and enthrall.
This section will delve into the intricacies of these adjustments, revealing the secrets to manipulating light and shadow to achieve the desired aesthetic effect.
Adjusting Image Brightness Levels
Brightness adjustment dictates the overall lightness or darkness of an image. It’s a fundamental tool for setting the stage and establishing the mood. Understanding the mechanics of brightness is essential for controlling the tonal range of your images. IrfanView provides a dedicated slider for adjusting brightness, allowing for incremental increases or decreases in luminance. By manipulating this slider, you can elevate or diminish the overall light intensity within the image.
A notable example is adjusting a low-light photo to reveal details previously obscured by darkness.
Methods for Adjusting Image Contrast
Contrast, the difference in light and dark areas, is crucial in defining the texture and details within an image. Manipulating contrast significantly alters the visual impact. IrfanView employs a similar slider-based approach for contrast adjustments. A higher contrast setting accentuates the difference between highlights and shadows, creating a more striking and dynamic image. Conversely, a lower contrast setting softens the image, creating a more subdued and uniform appearance.
An image of a landscape, for instance, might benefit from a higher contrast setting to highlight the dramatic variations in light and shadow.
Impact of Brightness and Contrast Adjustments on Image Appearance
Brightness and contrast adjustments profoundly influence the visual narrative of an image. Increased brightness often yields a brighter, more cheerful image, whereas decreased brightness produces a darker, more somber effect. Similarly, higher contrast accentuates details and textures, enhancing the visual impact, while lower contrast blurs the difference between light and dark, creating a softer aesthetic. A skilled editor judiciously utilizes these tools to achieve the desired visual effect.
A portrait might benefit from a slight contrast increase to highlight facial features.
Demonstration of Brightness and Contrast Adjustment Tools
IrfanView’s interface features dedicated sliders for brightness and contrast adjustments. These sliders allow for a precise, intuitive adjustment of these parameters. Dragging the brightness slider to the right increases the brightness of the image, and dragging it to the left decreases the brightness. Similarly, adjusting the contrast slider will accentuate or diminish the difference between light and dark regions within the image.
Comparison Table of Various Brightness and Contrast Adjustment Tools
| Tool | Mechanism | Ease of Use | Precision | Impact on Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IrfanView | Slider-based | High | Moderate | Subtle to significant, depending on adjustment |
Image Color Adjustments
Unleash the power of color manipulation! Within the digital realm of image editing, color adjustments are not merely cosmetic; they are instruments of artistic expression and communicative impact. Mastering these techniques empowers you to evoke specific moods, highlight crucial details, or dramatically transform the overall aesthetic of your images.
Color Balance
Color balance dictates the relative intensity of colors within an image. A perfectly balanced image ensures that colors appear natural and harmonious. Improper color balance can create a jarring and unnatural effect. IrfanView offers a sophisticated color balance tool, allowing for precise adjustments to red, green, and blue channels. By carefully adjusting these channels, you can neutralize unwanted color casts or create striking artistic effects.
This is akin to fine-tuning the tonal spectrum of a painting. The tool allows you to precisely control the individual color components.
Saturation
Saturation, the intensity of a color, is a crucial element in image aesthetics. Adjusting saturation can dramatically alter the vibrancy and boldness of an image. Over-saturation can lead to a garish appearance, while undersaturation can make an image appear dull and lifeless. Precise control over saturation allows you to sculpt the visual impact of your images, turning mundane scenes into dynamic artworks.
IrfanView offers intuitive saturation controls, permitting nuanced adjustments.
Hue
Hue, the color’s fundamental tone, is the aspect of color that distinguishes red from green or blue from yellow. Modifying hue can drastically alter the overall impression of an image, transforming landscapes into surreal scenes or portraits into abstract masterpieces. IrfanView’s hue adjustment tools allow for the subtle shifts that can transform a photograph into something entirely different.
This capability is analogous to mixing different pigments to achieve unique shades in a painting.
Color Adjustments in IrfanView
A comprehensive step-by-step guide to color modification within IrfanView:
- Open your desired image in IrfanView.
- Navigate to the “Edit” menu, then select “Color Adjustments.”
- Choose from a range of color adjustments, including “Color Balance,” “Saturation,” and “Hue.”
- Use the sliders to adjust the intensity of each color channel. For color balance, observe the image as you adjust the sliders. For saturation, observe how the vibrancy of the colors change. For hue, observe how the tones change.
- Experiment with various settings until you achieve the desired effect.
- Save your modified image.
Example: Color Adjustments on a Landscape, How to do basic editing in irfanview
Imagine a landscape photograph that appears slightly yellowish. By adjusting the color balance, you can neutralize the yellow tint and bring out the natural hues of the scene. This process can make the image appear more realistic and vivid. Adjusting the saturation will enhance the colors, making the foliage and sky more vibrant. Increasing the saturation can make the image more dynamic, but be cautious of over-saturation, which can lead to a garish appearance.
Example: Color Adjustments on a Portrait
Consider a portrait photograph where the subject’s skin tone appears slightly washed out. By adjusting the color balance and saturation, you can bring out the natural warmth of the skin tone, making the subject appear more vibrant and lifelike. Adjusting the hue might also be used to subtly change the color tones of the subject’s attire or background.
This will create a distinct impression, transforming the portrait into a work of art.
Basic Image Enhancement Techniques
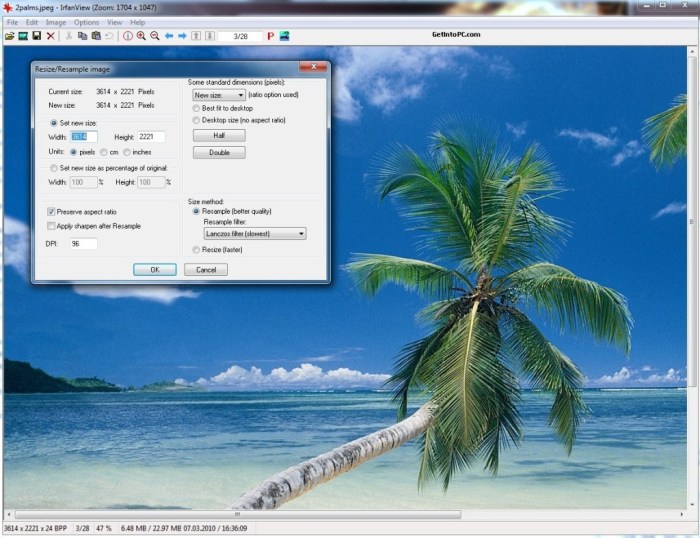
Unleash the latent detail within your digital images! Mastering basic image enhancement techniques empowers you to transform ordinary snapshots into extraordinary visuals, revealing hidden nuances and amplifying the impact of your work. This exploration delves into the realm of sharpening, smoothing, and filtering, equipping you with the tools to refine your images to perfection.Image enhancement, in essence, is the art of refining and refining images to highlight their essential characteristics.
It is about adjusting the image’s tonal values, sharpness, and color balance to achieve a visually appealing and informative outcome. This process can involve subtle alterations or dramatic transformations, depending on the desired aesthetic and the nature of the image itself.
Sharpening Techniques
Sharpening enhances the definition of edges and fine details in an image. This process increases the contrast between edges, making them stand out more prominently. Effective sharpening techniques can dramatically improve the visual appeal of an image, making it look more crisp and detailed.A common approach involves increasing the contrast between the high-frequency components of the image. These high-frequency components contain information about the edges and fine details of the image.
By enhancing these components, the image becomes sharper and more visually appealing. Sophisticated sharpening algorithms employ mathematical techniques to preserve the image’s overall clarity while accentuating its details.
Smoothing and Blurring Methods
Smoothing, or blurring, is the antithesis of sharpening. It reduces the visual impact of fine details and edges, creating a softer, more diffused look. This technique is often used to remove noise, blemishes, or imperfections from images, or to create a more artistic or painterly effect. Images may appear more muted and less defined.The process typically involves averaging pixel values in a localized region, effectively reducing the contrast between adjacent pixels.
Different blurring techniques use various averaging methods, impacting the level of blur and the degree of detail loss. Gaussian blur, for instance, uses a Gaussian function to distribute the averaging weights, resulting in a smooth, natural blur effect.
Basic Image Enhancement Filters
Filters are pre-programmed algorithms applied to images to achieve specific effects. They offer a convenient and versatile means of enhancing an image’s visual appeal.
- High-Pass Filters: These filters accentuate the high-frequency components of an image, boosting detail and sharpness. This technique works well for images that need an increase in sharpness or clarity. This technique enhances the contrast between edges and fine details.
- Low-Pass Filters: Conversely, these filters diminish high-frequency components, effectively blurring the image. This results in a softer, more diffused appearance, ideal for removing noise or creating a smooth, painterly effect. This technique is effective in reducing detail and creating a smoother image.
- Median Filters: These filters are particularly useful for reducing noise and preserving sharp edges. By replacing each pixel with the median value of its surrounding neighbors, median filters effectively eliminate isolated noise pixels while maintaining the integrity of important image features.
Filter Comparison Table
The effectiveness of each filter depends on the image and the desired outcome.
| Filter Type | Effect | Impact on Image Quality |
|---|---|---|
| High-Pass | Increases sharpness, enhances details | Can create a more crisp and detailed image, but excessive use can result in artificial or harsh edges. |
| Low-Pass | Reduces sharpness, smooths details | Can remove noise and create a softer, more diffused look, but excessive use can result in loss of important details. |
| Median | Reduces noise, preserves edges | Effective in removing noise without blurring important details. |
Impact on Image Quality
The choice of enhancement technique directly influences the quality of the final image. Excessive sharpening can lead to artifacts and a harsh appearance, while over-smoothing can result in a loss of crucial details. Careful consideration of the specific image characteristics and desired outcome is crucial. Understanding these effects is essential to achieving the desired result.
Saving Edited Images
Mastering the art of image editing hinges on the meticulous preservation of your creations. Saving your transformed visuals in the correct format is paramount, ensuring the fidelity and usability of your work. This crucial step will determine the final quality and file size of your edited masterpieces.The digital canvas demands a nuanced understanding of image formats. Each format, from the ubiquitous JPEG to the pristine PNG, possesses unique characteristics that impact file size and image quality.
This section will equip you with the knowledge to make informed choices when saving your meticulously crafted images.
Image Format Selection
Choosing the appropriate image format is crucial for maintaining both the visual integrity and file size of your edited images. JPEG, renowned for its compact file size, excels in capturing photographs, often sacrificing some image detail in the process. PNG, conversely, retains superior image quality but results in larger file sizes. GIF, optimized for simple graphics and animations, provides a balance between quality and file size, but it is less suited for complex imagery.
Impact of Image Formats on File Size and Quality
The selection of an image format directly impacts the final file size and quality. JPEGs, with their lossy compression, achieve significantly smaller file sizes but may exhibit some visible artifacts, particularly in areas of sharp detail. PNGs, using lossless compression, maintain superior quality but result in larger files. GIFs, optimized for simple graphics, strike a balance between file size and quality, but are limited in the range of colors and details they can represent.
Comprehending these trade-offs is essential for making effective choices.
Supported Image Formats in IrfanView
IrfanView supports a diverse range of image formats, empowering users to seamlessly integrate a wide variety of files into their editing workflow. The software’s comprehensive support for common formats such as JPEG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, BMP, and more ensures that users can effectively manage and manipulate a variety of image types. This extensive compatibility is a key feature for users working with a diverse range of image sources.
- JPEG (JPG): Excellent for photographs, achieving small file sizes while maintaining acceptable quality for most applications. Lossy compression is its defining characteristic.
- PNG: Ideal for images with intricate details and transparency. PNG’s lossless compression preserves every pixel, resulting in higher quality but larger files.
- GIF: Suitable for simple graphics and animations. GIFs use lossless compression and are often used for web graphics and animations.
- TIFF: Preserves image quality without compression, resulting in large file sizes. TIFFs are useful for archival purposes and applications demanding uncompromised quality.
- BMP: A simple format that is widely supported but often results in large file sizes. BMP is best for applications requiring compatibility across various systems.
Examples of Saving Images in Various Formats
To illustrate the practical application of these formats, consider the following examples. Saving a high-resolution photograph as a JPEG will result in a smaller file size but may introduce slight image degradation. Saving a logo as a PNG will preserve the image’s details and maintain its quality, but the file size will be larger. Saving a simple graphic as a GIF will create a small file with the graphic’s characteristics retained.
| Format | Description | Use Case | Impact on File Size | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Lossy compression | Photographs | Small | May have artifacts |
| PNG | Lossless compression | Graphics, logos | Large | High |
| GIF | Lossless compression | Simple graphics, animations | Medium | Limited color palette |
Working with Multiple Images
Unleash IrfanView’s power to conquer the digital image realm. Harness its capabilities for batch processing, streamlining your workflow and achieving unparalleled efficiency. Mastering this technique elevates you from a simple image editor to a true digital artisan.
Opening and Editing Multiple Images Simultaneously
IrfanView empowers you to open and edit multiple images concurrently. This revolutionary approach dramatically accelerates your editing process, transforming hours of individual edits into mere minutes. Select multiple images by holding the Ctrl key while clicking on them. Once selected, the images are loaded into IrfanView, ready for your creative touch. You can then apply the same editing commands to all images simultaneously.
Batch Processing Images: A Symphony of Efficiency
Batch processing, a cornerstone of IrfanView’s capabilities, allows you to apply identical edits to numerous images. This mode automates repetitive tasks, transforming a tedious chore into a streamlined process. IrfanView’s batch mode offers a unique opportunity to transform a stack of images with consistency and efficiency. Imagine effortlessly applying the same adjustments to a collection of photos, all at once.
Advantages of Working with Multiple Images Simultaneously
Working with multiple images concurrently in IrfanView offers significant advantages. Time savings are paramount. Applying identical edits to a batch of images saves valuable time compared to manually editing each image individually. This streamlined approach minimizes errors and ensures consistency in edits. This consistency ensures your images maintain a unified aesthetic.
IrfanView’s Batch Processing Tools
IrfanView’s batch processing tools are indispensable for bulk editing. These tools allow for the application of various editing commands, such as resizing, cropping, rotating, and color adjustments, to multiple images. This functionality empowers you to rapidly achieve uniformity in your image collections.
Table of Batch Editing Options
| Editing Option | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Resize | Adjusts the dimensions of images. | Uniformly resizing a set of photos for a website gallery. |
| Crop | Removes unwanted portions of an image. | Removing excess background from a collection of product images. |
| Rotate | Turns an image by a specified angle. | Correcting orientation of a batch of scanned documents. |
| Brightness/Contrast | Adjusts the light and darkness of an image. | Ensuring consistent lighting across a series of photographs taken in different conditions. |
| Color Adjustments | Modifies the colors in an image. | Creating a cohesive color palette across a portfolio of images. |
Conclusive Thoughts: How To Do Basic Editing In Irfanview
Mastering basic editing in IrfanView equips you with essential tools to refine and enhance your digital images. This guide has provided a solid foundation for working with this powerful, user-friendly application. Now you can confidently crop, resize, rotate, adjust colors, and enhance your images, achieving professional-quality results without complex software.
FAQ Compilation
What image formats does IrfanView support for saving edited images?
IrfanView supports a wide range of image formats, including JPG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, BMP, and more. The specific formats supported may vary slightly depending on the IrfanView version.
How can I batch edit multiple images in IrfanView?
IrfanView offers a powerful batch processing mode that allows you to apply the same editing operations to multiple images simultaneously. This significantly speeds up your workflow, particularly for large image sets.
What are the advantages of using IrfanView for basic image editing?
IrfanView is lightweight, fast, and boasts an intuitive interface. This makes it an excellent choice for basic image editing tasks. Its straightforward features allow you to quickly accomplish essential edits without complex learning curves.
Can IrfanView handle large image files effectively?
IrfanView is generally capable of handling large image files, but performance may vary depending on the file size and your computer’s specifications. For extremely large files, consider using specialized software for advanced editing and processing.
