How to fix a ac tuen handel valve – How to fix a AC return/supply valve is a crucial skill for anyone maintaining their air conditioning system. Malfunctioning valves can lead to significant issues, from reduced cooling efficiency to complete system failure. This guide will walk you through the process of identifying the problem, gathering the necessary tools, disassembling the valve, inspecting components, replacing parts (if needed), reassembling, and finally testing the system.
Understanding these steps can help you address these problems effectively and avoid costly repairs.
This comprehensive guide will cover the entire process from initial troubleshooting to final system verification, ensuring you understand each step and are able to effectively handle any issues that arise. We’ll explore various valve types, common problems, and the troubleshooting procedures necessary for a successful repair.
Identifying the Issue
Right, so AC return/supply valves, these aren’t exactly rocket science, but they can give you a right headache if they go pear-shaped. Understanding the common problems and symptoms is key to getting your AC system back on track. Basically, these valves control the flow of air, and if they’re not working properly, your whole system suffers.AC return/supply valves are essential components in any air conditioning system, regulating the airflow of cool air into your space and the removal of warm air.
Malfunctions can lead to uneven temperature distribution, reduced cooling efficiency, and potentially, expensive repairs down the line.
Common Problems with AC Valves
AC return/supply valves, like any mechanical component, can experience various issues. Leaks in the valve seals are a common problem, leading to airflow issues and a loss of refrigerant. Clogged filters or debris build-up in the valve can restrict airflow, reducing efficiency and potentially causing the valve to malfunction. Corrosion and rust are also potential problems, especially in older systems, leading to restricted airflow and valve damage.
Incorrect installation or improper maintenance practices can also contribute to these problems.
Symptoms of a Malfunctioning AC Valve
Recognising the symptoms of a faulty AC valve is crucial for prompt diagnosis and repair. Noticeable symptoms include uneven room temperatures, a significant drop in cooling performance, strange noises coming from the AC unit, or a noticeable lack of airflow in certain rooms. You might also see condensation pooling around the AC unit, which could indicate a leak or pressure issue.
If you’re getting all these symptoms, it’s time to investigate the valve.
Types of AC Return/Supply Valves and Potential Failure Points
Different types of valves exist, each with its own potential failure points. Ball valves are simple, but their seals can wear down over time, causing leaks and restricting airflow. Butterfly valves, while efficient, can suffer from sticking or binding issues, preventing proper airflow regulation. Diaphragm valves offer a higher level of precision but are more susceptible to damage from pressure fluctuations.
Comparative Analysis of AC Valve Types
| Valve Type | Common Problems | Troubleshooting Steps | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | Leaking seals, sticking ball, debris build-up | Inspect seals for wear, check for obstructions, verify proper lubrication | Replace seals, clean valve, lubricate if necessary |
| Butterfly Valve | Sticking, binding, damaged actuator, leaks in shaft seals | Inspect for binding, check actuator operation, verify seal integrity | Lubricate actuator, replace actuator, replace shaft seals |
Gathering Tools and Materials: How To Fix A Ac Tuen Handel Valve
Right, so you’ve nailed identifying the problem with that AC return/supply valve. Now, let’s get down to the nitty-gritty of the tools and parts needed for the fix. This section lays out everything you’ll need, from basic hand tools to potentially specialised HVAC gear. Crucially, it also covers safety precautions – essential for any work involving compressed air and electrical components.Understanding the specific repair needed is key.
Different issues call for different tools and replacement parts. A simple valve handle replacement is a different kettle of fish compared to a complete valve overhaul. The table below details potential scenarios and the necessary gear.
Required Tools and Parts
This is the lowdown on the tools and replacement parts required for different AC valve repair scenarios. Knowing which tools you need will save you a load of hassle and time.
| Repair Scenario | Required Tools | Replacement Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Valve Seal Replacement | Adjustable wrench, crescent wrench, needle-nose pliers, pipe wrench (if necessary), flathead screwdriver, valve seal replacement kit (containing new seals, potentially gaskets), cleaning rags/wipes. | New valve seal(s), possibly gaskets. |
| Valve Handle Replacement | Screwdriver (Phillips or flathead, depending on the valve), adjustable wrench, pliers, replacement valve handle. | New valve handle, potentially retaining screws/washers. |
| Complete Valve Replacement | Adjustable wrench, crescent wrench, pipe wrench (if necessary), socket set (for various bolt sizes), torque wrench (highly recommended), new valve. | New AC return/supply valve. |
Safety Precautions
Working with AC systems involves potential hazards. Always prioritise safety. Before starting any repair, ensure the AC unit is powered down and the system is depressurised. This is paramount to prevent injury from compressed gas or electric shock. If you’re not entirely confident with the procedures, consult a qualified HVAC technician.
Don’t be a hero – safety first.
Disassembling the Valve
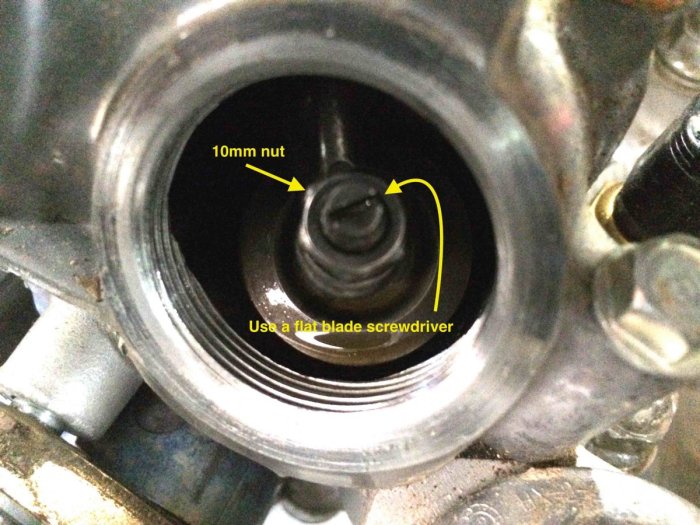
Right, so you’ve got the AC return/supply valve looking a bit dodgy. Time to get your hands dirty and get it sorted. This section covers the safe and systematic dismantling process. Remember, safety first! Incorrect procedures can lead to serious issues, so follow these steps meticulously.
Safe Disconnection of the AC Return/Supply Valve
Before touching anything, ensure the system is powered down. This prevents electrical shocks and potential damage to components. Locate the power supply connection for the AC unit and carefully disconnect it. Mark the connection with a label or take a photo to ensure proper reconnection. Afterward, isolate the valve from the rest of the system by closing any valves in the line to prevent refrigerant leaks.
Removing the Valve from its Housing
This part requires careful handling to avoid damaging the valve or its housing. First, identify any securing mechanisms, such as screws, clamps, or clips. Use the appropriate tools (screwdrivers, pliers, etc.) to loosen and remove these fasteners. Pay close attention to the orientation and position of the components. Take photos or make notes as you go.
This will aid in reassembly. Once all fasteners are removed, gently pull the valve out of its housing, taking care not to damage the connections or seals.
Disassembly Steps
This section Artikels the systematic steps for disassembling the valve, emphasising crucial points. Improper disassembly can lead to damage and necessitate costly replacements.
- Step 1: Disconnect Power and Secure the Area. Ensure the power to the AC unit is completely disconnected. Mark the connections for easy reassembly. Secure the area to prevent any accidental movement or disturbance. This precaution prevents accidents and damage to components.
- Step 2: Isolate the Valve from the System. Close any valves in the refrigerant lines that connect to the valve. This isolates the valve from the rest of the system, preventing refrigerant leaks. Using a valve key is vital for this task. Failure to isolate the valve can result in a release of refrigerants, which can damage the environment.
- Step 3: Remove Securing Fasteners. Carefully remove any fasteners securing the valve to its housing. Use the appropriate tools, such as screwdrivers or pliers. Record the position and orientation of each component to aid in reassembly. Incorrectly removing these fasteners can result in damage to the housing or the valve.
- Step 4: Gently Extract the Valve. Carefully remove the valve from its housing. Use caution to avoid damaging the valve or its connections. Take your time and be precise. Damage to the valve or its connections could lead to inefficient operation of the AC unit.
- Step 5: Inspect and Document. Examine all components for signs of damage or wear. Take photos or make notes of any observed issues or unusual markings. Thorough inspection ensures a proper understanding of the valve’s current state.
Disassembly Procedure Table
| Step | Action | Image Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Disconnect power to the AC unit using the correct tools. Ensure all connections are properly labeled and marked for easy reassembly. | An image showing the power cord disconnected from the AC unit. The connections are clearly labeled and marked. |
| 2 | Close the valves in the refrigerant lines connected to the valve. This isolates the valve from the rest of the system, preventing refrigerant leaks. | An image of the valves in the refrigerant lines being closed. The valve key is visible. |
| 3 | Carefully remove any securing fasteners. Note the orientation of each component. | An image showcasing the removal of screws or clips securing the valve to the housing. Tools are correctly positioned and used. |
| 4 | Gently pull the valve from its housing, taking care not to damage the connections. | An image depicting the valve being extracted from its housing. The valve is being carefully pulled out. |
| 5 | Inspect all components for damage and document any issues. | An image showing a close-up inspection of the valve and its components. The inspector is checking for damage or wear. |
Inspecting and Diagnosing the Problem

Right, so you’ve got the valve disassembled, now it’s time to suss out the issue. This stage is crucial; a proper diagnosis prevents you from replacing parts unnecessarily. A thorough inspection will pinpoint the exact problem, saving you time and money.
Visual Inspection of Components
A systematic visual check is key. Carefully examine each part for signs of damage. Look for cracks, chips, or any deformation in the metal components. Check the seals for wear and tear; any signs of significant wear, like grooves or splitting, should be noted. Pay attention to the condition of the handle and any connections.
Even a small hairline crack can lead to a major issue.
Common Issues During Inspection
Identifying potential problems early on saves a lot of hassle later. Here’s a list of common issues that can be identified during a visual inspection:
- Cracked or fractured valve body.
- Worn or damaged seals (O-rings, gaskets). These are often the culprit behind leaks.
- Bent or broken valve stem or handle.
- Corrosion on metal parts, which can weaken them.
- Loose or damaged connections.
- Obstructions or debris lodged within the valve.
A thorough check is important to understand the potential problem, not just finding one symptom.
Diagnosing the Root Cause
Just finding damage isn’t enough; we need to understandwhy* the valve isn’t working. This involves testing and comparison. Consider the operational history of the valve. Has it been used heavily recently? Has there been a change in the fluid being used?
- Leak testing: A leak test helps pinpoint the exact location of a leak. Use soapy water to identify air bubbles, which indicate leakage points. Note the exact location of leaks, as this can help diagnose the problem.
- Pressure testing: This method can identify structural issues, such as cracks or weakened parts. A pressure gauge and a safe pressure level are necessary.
- Comparison with diagrams: Referencing manufacturer diagrams is vital. This ensures you’re examining the right parts and checking for standard dimensions.
- Identifying the type of fluid: Different fluids have different effects on seals and components. Knowing the type of fluid used in the system is important.
Identifying Specific Problems with Parts, How to fix a ac tuen handel valve
Pinpointing the exact part causing the issue is essential.
- Worn Seals: Check the seals for signs of wear. If the seals are worn, they’ll likely be leaking. A visual inspection can confirm this.
- Damaged Handles: Examine the valve handle for any cracks, bends, or loose connections. A damaged handle may be a symptom of a more significant underlying issue or simply indicate a weak point that could be a future problem.
This is crucial; the right diagnosis is the first step towards a swift and efficient repair.
Replacing Parts (if needed)
Right, so you’ve diagnosed the problem, now it’s time to get your hands dirty and swap out any faulty components. This section will guide you through the process of replacing worn-out or damaged parts, ensuring a proper installation and reassembly. Proper part replacement is crucial for the valve’s longevity and efficient operation.Replacing parts involves careful attention to detail, ensuring that each component is installed correctly to avoid leaks and ensure the valve functions as intended.
A thorough understanding of the specific valve’s design is essential to avoid making errors during the replacement process.
Replacing Valve Seals
The valve seal is a critical component, often the culprit behind leaks. A worn or damaged seal can lead to poor performance and potential damage. To replace it, you need the correct replacement seal.
- Ensure the old seal is completely removed, cleaning the sealing surface thoroughly to remove any debris or residue. This is essential for a proper seal.
- Position the new seal onto the valve housing, ensuring it aligns correctly with the existing grooves. A properly positioned seal is essential for the valve to work correctly.
- Apply a thin layer of appropriate lubricant to the seal’s perimeter, facilitating smooth operation and preventing friction. Proper lubrication is key for the seal to function correctly.
Replacing the Actuator (if applicable)
If the actuator is faulty, you’ll need to replace it. Actuators control the valve’s movement, so a malfunctioning one can result in poor control and potential damage.
- Carefully disconnect the actuator from the valve, ensuring that all electrical connections are properly isolated and disconnected.
- Position the new actuator into the valve housing, ensuring it aligns correctly with the existing mounting points. Misalignment can lead to issues with the actuator’s operation.
- Reconnect the actuator to the valve, ensuring that all electrical connections are securely reconnected and that the actuator is properly seated. Verify that the connections are correct to avoid electrical problems.
Reassembling the Valve
Following the proper reassembly sequence is crucial to prevent issues with the valve’s operation. Incorrect reassembly can lead to leaks or malfunctions.
- Place the valve body and cover onto the valve housing, ensuring they are properly aligned and secured.
- Tighten the mounting screws, ensuring even pressure is applied and that the components are firmly attached.
- Check for any leaks around the joints using a leak detection solution. This is vital for ensuring the valve functions correctly.
Compatibility Table
| Part Name | Description | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Valve Seal | A rubber or synthetic o-ring or gasket that creates a seal between components. | Ensure the dimensions of the new seal match the old seal to guarantee a proper fit. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for exact compatibility details. |
| Actuator | The component that moves the valve. | Compatibility depends on the valve’s specific model and specifications. Consult the manufacturer’s part list or the valve’s documentation. |
| Mounting Screws | Securing components to the valve body. | Ensure the correct size and type of screws are used, as improper use can lead to damage. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications. |
Reassembling the Valve
Right, so you’ve wrestled with the valve, identified the issue, and replaced any dodgy bits. Now, it’s time to put it all back together like a pro. Remember, precision is key here; a misaligned component could lead to a whole heap of issues down the line. Getting it spot on is paramount.
Reconnecting the AC Return/Supply Valve
To reconnect the valve, ensure the O-rings and seals are in good nick. A worn or damaged seal will compromise the airtightness of the system, potentially causing leaks and reduced efficiency. Check each component for any visible damage or signs of wear. If anything looks questionable, replace it immediately. This is crucial for long-term performance.
Correctly Aligning and Securing the Valve
Precise alignment of the valve housing is vital. Incorrect alignment can lead to leaks and uneven airflow. Use a dial gauge or similar precision tool to ensure the valve is centered and properly seated in the housing. Tighten the securing bolts progressively, in a star pattern, to prevent distortion and ensure even clamping pressure across the valve body.
Over-tightening can cause damage to the threads or the valve housing itself. It’s all about finding that sweet spot between secure and safe.
Testing the Valve Post-Reassembly
Once the valve is reassembled, it’s time for a thorough test. Begin by checking for leaks around the valve housing and connections. Apply soapy water to all joints and look for bubbles. No bubbles means a good seal. Next, activate the AC system and monitor the airflow.
Ensure the valve is regulating the flow as intended. Any unusual noises or uneven airflow could indicate a problem that needs further attention.
Reassembly Steps Summary
| Step | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Align valve housing with the return/supply line using a dial gauge to ensure precise centering. | Ensure the valve is properly aligned to prevent leaks and uneven airflow. |
| 2 | Carefully reinsert the O-rings and seals into their respective positions. | Confirm that O-rings and seals are in good condition. Replace if damaged. |
| 3 | Tighten the securing bolts in a star pattern to avoid distortion and ensure even clamping pressure. | Tighten bolts progressively, avoiding over-tightening. |
| 4 | Inspect for leaks by applying soapy water to all joints and connections. | No bubbles indicate a good seal. |
| 5 | Activate the AC system and monitor airflow. | Ensure the valve regulates flow as intended. |
Testing and Verification
Right, so you’ve wrestled with the valve, now it’s time to see if your handiwork actually works. Proper testing is crucial to ensure a smooth AC operation and avoid further headaches down the line. This section will cover the vital steps for verifying your repair.
Testing the AC System
The AC system needs a thorough test to confirm the repaired valve’s effectiveness. First, switch the system on and monitor the refrigerant flow. Observe if the compressor cycles correctly and the condenser fan operates as expected. This initial check will quickly identify any glaring issues.
Expected Functionality of a Return/Supply Valve
A correctly functioning AC return/supply valve will allow the refrigerant to flow smoothly between the evaporator and compressor. This ensures the system maintains the proper pressure and temperature differentials. The valve’s response should be immediate and consistent, with no noticeable fluctuations. Any delays or inconsistent operation could point to a lingering issue.
Verification Checklist
This checklist ensures all aspects of the repair are accounted for, like a proper QA check.
- Compressor operation: Confirm the compressor starts and runs consistently, indicating a stable refrigerant flow.
- Condenser fan operation: Ensure the condenser fan functions, which is essential for proper heat dissipation and efficient system cooling.
- Refrigerant level: Verify the refrigerant level is within the optimal range. Low refrigerant levels will affect the AC’s performance. Consider using a gauge for precision.
- Pressure readings: Take pressure readings at key points in the system, comparing them to manufacturer specifications. Deviations from the expected values can indicate a leak or improper valve function.
- Temperature differentials: Observe the temperature difference between the evaporator and condenser. A significant difference signifies that the refrigerant is flowing as expected.
- System response: Assess the AC’s response to changing environmental conditions, ensuring a rapid and effective cooling effect.
Monitoring the AC System Post-Repair
Monitoring the AC system post-repair is vital for early detection of any emerging problems. Proactive monitoring allows for timely intervention before the issue escalates.
- Regular checks: Schedule regular checks on the AC system to monitor pressure, temperature, and other key parameters. A weekly or bi-weekly check is a good practice.
- System logs: Keep a log of all readings and observations to track any potential patterns or trends. This historical data will prove valuable for troubleshooting.
- Leak detection: Implement a leak detection procedure to quickly identify any refrigerant leaks. A leak detection kit is handy for this purpose.
- Environmental factors: Be mindful of environmental factors like ambient temperature. High ambient temperatures can place increased stress on the AC system.
- Addressing issues: Address any observed issues promptly to prevent further problems and maintain optimal AC performance.
Final Summary
Successfully repairing an AC return/supply valve requires a methodical approach, from initial diagnosis to final system testing. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently address these issues, ensuring your AC system functions optimally. Remember to prioritize safety throughout the process and consult professionals if needed. This guide provides a solid foundation for handling these repairs effectively.
Clarifying Questions
What are the most common causes of AC return/supply valve malfunction?
Common causes include worn seals, damaged handles, obstructions in the valve, and issues with the valve’s internal components. Sometimes, a malfunctioning valve is a symptom of a larger problem in the AC system, such as a refrigerant leak.
What safety precautions should I take when working on AC systems?
Always disconnect the power supply to the AC unit before starting any repair work. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses. Be cautious of sharp edges and potential refrigerant leaks. If unsure about any step, consult a qualified HVAC technician.
How do I know if a replacement part is compatible with my valve?
Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or diagrams for the correct part numbers and dimensions. Compatibility charts and diagrams should be available with replacement parts or from the manufacturer’s website.
What are the signs of a leak in the AC system?
Unusual noises, reduced cooling capacity, visible liquid around the AC unit, or a noticeable drop in refrigerant levels can all indicate a leak. Always be cautious of refrigerant as it can be harmful.
