How to move task manager to another screen? This guide provides a comprehensive overview of relocating your task manager window to a different screen on various operating systems, detailing methods, troubleshooting, and advanced customization options. Understanding how to reposition the task manager can significantly improve workflow efficiency and screen real estate utilization.
From simple re-positioning to advanced configurations, this guide covers all bases. The process varies slightly between operating systems, but the core principles remain consistent. Learning these techniques can lead to a more productive digital environment.
Introduction to Task Manager Relocation
Unlocking the full potential of your operating system often involves strategic placement of crucial tools. Moving the Task Manager to a different screen can be a game-changer, improving workflow and productivity. This newfound flexibility can streamline your multitasking and enhance your overall digital experience.Relocating the Task Manager isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about optimizing your digital environment. By placing it on a secondary monitor or a dedicated screen area, you create a more efficient workspace.
This often results in a faster response to task-related issues, better organization, and less screen clutter. Imagine having quick access to system resources without constantly shifting your focus between windows – that’s the power of strategic placement. Common scenarios like frequent system monitoring or handling multiple applications simultaneously benefit immensely.
Benefits and Use Cases
The strategic placement of the Task Manager offers a variety of advantages. For instance, a dedicated secondary screen for Task Manager allows for continuous monitoring without obstructing your primary workspace. This is invaluable for system administrators or anyone managing multiple applications simultaneously. The improved workflow leads to reduced switching time between tasks, which directly translates into increased productivity.
Furthermore, the minimized visual clutter on your primary screen enhances focus and attention span, leading to a more streamlined workflow.
Common Scenarios for Relocation
Relocating the Task Manager becomes particularly beneficial in several common scenarios. For instance, in scenarios where you are running multiple applications simultaneously, having the Task Manager on a separate screen prevents visual interference and enhances multitasking. Dedicated system administrators often find it beneficial to keep the Task Manager on a separate screen to monitor system processes without interrupting ongoing work.
Similarly, those who frequently work on multiple programs or require detailed system insights will find this feature invaluable. The Task Manager’s relocation enables a smoother and more efficient workflow.
Operating System Window Management
Understanding how different operating systems manage windows is crucial for effective relocation. Each operating system has its own unique approach to window placement and manipulation. Windows, for example, utilizes a comprehensive window management system that allows for multiple windows on different screens. This system offers significant flexibility for customizing the workspace.
- Windows: Windows provides intuitive options for arranging windows across multiple monitors, enabling users to place the Task Manager on a separate screen with ease. Adjustments can be made through the display settings or using window management features.
- macOS: macOS employs a similar approach, leveraging window management features for flexibility in positioning and resizing windows. These features allow for a streamlined workspace setup, including the placement of the Task Manager.
- Linux: Linux distributions offer varying degrees of window management, depending on the chosen desktop environment. Some environments provide comprehensive options for arranging windows and managing screens, ensuring the Task Manager can be relocated effectively.
Methods for Moving Task Manager
Unlock the power of your operating system’s layout by effortlessly relocating your Task Manager to a different screen. This newfound flexibility allows for a more ergonomic workspace, maximizing screen real estate and streamlining your workflow. Moving your Task Manager is a simple yet impactful change that can elevate your productivity.Relocating the Task Manager isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about optimizing your digital environment.
This streamlined approach will help you focus on the tasks at hand, eliminating unnecessary distractions.
Windows Task Manager Relocation
Windows offers a straightforward approach to repositioning the Task Manager. Utilizing the operating system’s built-in features empowers users to effortlessly customize their workspace, enhancing efficiency and comfort.
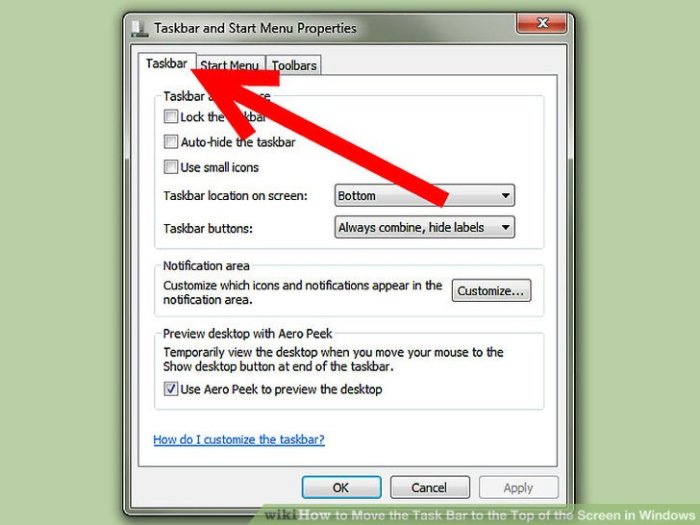
- Using the Windows Snap feature: This method involves dragging and dropping the Task Manager window to the desired location on a different screen. Locate the Task Manager window, click and drag it toward the other screen, holding the mouse button until the window fully transitions. This method works best for displaying the Task Manager on a secondary monitor, particularly when the primary monitor is occupied by other applications.
- Employing the taskbar’s options: Right-click the Task Manager icon on the taskbar. A contextual menu appears, offering options for moving the Task Manager window. Select “Move to” followed by the screen you want to relocate it to. This method allows for precise control over the Task Manager’s location.
- Utilizing Display Settings: The Windows display settings offer comprehensive control over screen arrangements. This approach is ideal for users who want to fine-tune the Task Manager’s position and monitor layout for optimal usability. Open Display Settings, select the screen you want the Task Manager on, and use the options to move the Task Manager. This is highly effective for setting up a consistent arrangement across multiple screens.
macOS Task Manager Relocation
macOS utilizes a unique approach for managing the display of system-level information. Leveraging the built-in features empowers users to effectively customize their workspace, enhancing efficiency and comfort.
- Employing the window-resizing feature: This method involves dragging the window’s edges or corners to resize the Task Manager window to fit the desired space on the alternate screen. Dragging and adjusting the Task Manager window’s edges or corners allows for seamless transitions between screens, offering a visual and ergonomic optimization.
Chrome OS Task Manager Relocation, How to move task manager to another screen
Chrome OS offers a streamlined approach to task management. Utilizing the operating system’s built-in features empowers users to customize their workspace effectively, enhancing efficiency and comfort.
- Using the window-resizing feature: This method involves dragging the window’s edges or corners to resize the Task Manager window to fit the desired space on the alternate screen. Dragging and adjusting the Task Manager window’s edges or corners allows for seamless transitions between screens, offering a visual and ergonomic optimization.
Specific Operating System s: How To Move Task Manager To Another Screen
Let’s dive into the exciting world of moving your Task Manager across different operating systems! Each platform offers unique and often ingenious methods for relocating this vital system tool. We’ll explore the specifics, detailing the keystrokes and steps needed to seamlessly shift your Task Manager window to the desired screen. Get ready to master these techniques!Navigating the complexities of each OS can be daunting, but with our clear and concise explanations, you’ll be a Task Manager relocation pro in no time! Understanding the nuances of each operating system’s user interface is key to performing this task efficiently.
We’ll break down the processes for Windows, macOS, and (where applicable) Linux, providing step-by-step instructions for optimal results.
Windows Task Manager Relocation
Windows Task Manager, a fundamental part of the system, offers several ways to reposition its window. These methods provide maximum flexibility and control.
- Using the Window Controls: The most straightforward approach involves utilizing the standard window controls (minimize, maximize, close, and the drag-and-drop functionality). Clicking and dragging the Task Manager window’s title bar allows for easy repositioning across your monitor’s screen. This method is intuitive and requires minimal effort, making it ideal for quick adjustments.
- Keyboard Shortcuts for Windows Task Manager: While not directly for repositioning, you can utilize keyboard shortcuts for minimizing, maximizing, and closing the Task Manager window. This can be useful in conjunction with the drag-and-drop method for quick positioning, saving valuable time.
macOS Task Manager Relocation
macOS, known for its intuitive interface, offers a different but equally efficient approach to relocating the Activity Monitor (macOS’s equivalent of Task Manager).
- Utilizing the Window Controls: Similar to Windows, the Activity Monitor window can be repositioned by clicking and dragging its title bar. This method allows for a quick and easy shift to the desired display.
- Using the System Menu Bar: macOS offers additional methods to manage the Activity Monitor. Some users find using the menu bar to bring up the window, followed by the drag-and-drop functionality, quite effective for positioning it efficiently.
Linux Task Manager Relocation (if applicable)
Linux distributions vary significantly in their Task Manager implementations. Some employ graphical interfaces that offer similar relocation options as Windows or macOS, while others might utilize text-based terminal commands.
- Graphical Interface Approaches: Most modern Linux distributions use graphical desktop environments (GNOME, KDE, etc.). These environments typically allow for the same drag-and-drop functionality as Windows and macOS for relocating the Task Manager window (or equivalent tools).
- Command Line Options (for specific systems): For those using a terminal-based approach, the method for relocating the Task Manager will depend on the specific program used. In some cases, specific command-line options or keyboard shortcuts might allow for repositioning.
Efficiency Comparison
The efficiency of each OS’s method depends heavily on individual preference and the specific user interface in use. Windows’ direct drag-and-drop functionality is generally the fastest and most straightforward. macOS’s approach, leveraging the menu bar, offers an alternative that can be quite effective. Linux’s methods vary significantly, from simple drag-and-drop to more complex terminal-based options.
Advanced Configurations and Customization
Unlock the full potential of your Task Manager relocation! We’re diving deep into advanced settings, empowering you to fine-tune the placement and behavior of your Task Manager, ensuring a seamless and personalized experience. Imagine effortlessly configuring your Task Manager to always reside on your secondary monitor, or even automating the relocation process based on your schedule. Let’s explore these possibilities.Beyond basic relocation, advanced configurations provide granular control over the Task Manager’s behavior, preventing unwanted reversions to default locations and enabling efficient management of this vital system tool.
Customizing Task Manager Placement
Advanced settings often allow users to lock the Task Manager’s position on a specific screen. This ensures it consistently resides on the desired monitor, eliminating the frustration of unexpected returns to the default screen. By permanently pinning the Task Manager to a particular monitor, you can streamline your workflow and avoid any unwanted repositioning.
Preventing Default Screen Reversion
Task Manager settings often include options to prevent automatic repositioning to the default screen. This feature is crucial for maintaining consistent workspace layouts. By disabling this automatic reversion, you can retain the chosen screen location, maintaining a clutter-free environment and optimizing your productivity. Examples of this include configuring the Task Manager to always remain on a secondary display or setting a specific location and preventing any automatic repositioning.
Automating Relocation Processes
Imagine automating the Task Manager’s relocation based on your schedule or specific events. This can be accomplished using scripting languages, system utilities, or third-party automation tools. For example, you could configure a script to move the Task Manager to a specific screen at a particular time of day, or upon launch of a specific application. This level of customization ensures the Task Manager is always in the optimal location for your work style.
Potential Conflicts and Workarounds
Moving the Task Manager can occasionally introduce conflicts with other applications. These conflicts may involve overlapping windows or applications interfering with the Task Manager’s positioning. It is crucial to identify and understand these potential conflicts to resolve them effectively. For instance, if a program frequently utilizes the same screen area as the Task Manager, careful adjustment of window sizes or using a virtual desktop arrangement could be necessary.
Consider the potential overlap of application windows, and the Task Manager’s need for screen real estate to function optimally.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Relocating your Task Manager might seem straightforward, but occasionally, you encounter hiccups. Understanding these common issues and their solutions is crucial for a smooth and seamless experience. This section dives deep into potential problems and provides effective remedies, ensuring your Task Manager is always readily available on the screen you want it to be.
Task Manager Not Moving
Sometimes, the Task Manager stubbornly refuses to relocate. This could stem from various reasons, including conflicting settings, corrupted system files, or even a simple oversight. Troubleshooting requires a systematic approach.
- Verify the Display Settings: Ensure your desired display settings are properly configured. Check if the screen resolution or display mode might be hindering the move. Refresh the display settings to update any cached data.
- Check for Conflicts with Other Applications: In some cases, applications might be competing for system resources or interfering with the Task Manager’s relocation process. Try closing other programs to see if this resolves the issue.
- Run System File Checker (SFC): A corrupted system file can often cause problems with Task Manager relocation. Using the System File Checker tool can identify and repair corrupted files. This is a crucial step to ensure the integrity of your operating system.
Task Manager Disappearing
The Task Manager vanishing after relocation is another common problem. This could indicate a configuration error or an issue with the display driver.
- Restart the Task Manager: A simple restart of the Task Manager can often resolve temporary glitches. Close the Task Manager and then reopen it to see if this restores its location.
- Update Display Drivers: Outdated or corrupted display drivers can cause instability, potentially leading to the Task Manager disappearing. Updating the drivers to the latest version can solve this issue. Check the manufacturer’s website for the most up-to-date version.
- Check for Hardware Conflicts: Sometimes, hardware issues, such as a malfunctioning graphics card, can cause the Task Manager to vanish. If the problem persists, consider checking the hardware for potential conflicts.
Troubleshooting on Specific Operating Systems
Different operating systems might have slightly varying approaches to troubleshooting.
- Windows: Utilize the Windows Task Manager’s built-in features to diagnose and resolve issues related to its location. This might involve verifying display settings and restarting the Task Manager itself.
- macOS: Use Activity Monitor to manage processes and diagnose problems with the Task Manager’s placement. Check if there are any conflicting applications that might be interfering with the Task Manager’s location on the screen.
- Linux: The specific troubleshooting steps for Linux will depend on the desktop environment used. If the Task Manager isn’t moving, ensure the correct configurations are set for display management within the desktop environment. Check for conflicts with other applications running on the system.
Preventing Task Manager Relocation Issues
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the chances of encountering problems.
- Regular System Maintenance: Performing regular maintenance, including checking for updates and cleaning up unnecessary files, can improve system stability and prevent potential relocation issues.
- Proper Display Configuration: Ensure your display settings are optimized for your system and that no conflicts exist between different applications or hardware components.
- Compatibility Checks: Always verify the compatibility of new software or hardware with your current system configuration before installing or connecting them.
Organizing Information for Different Platforms
Mastering the art of relocating your Task Manager across different operating systems is a crucial skill for streamlined workflow. Knowing the nuances of each platform allows you to tailor your approach for optimal efficiency and productivity. This section dives into the specific methods for Windows, macOS, and Linux, offering detailed instructions and insightful examples.
Platform-Specific Task Manager Relocation Methods
Different operating systems utilize varying approaches to relocating the Task Manager window. Understanding these differences is key to quickly and easily adjusting your workspace. This section presents a structured comparison across Windows, macOS, and Linux.
| OS | Method 1 | Method 2 | Method 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows | Dragging the Task Manager window to the desired screen. | Using the built-in “Move to Screen” feature in the Task Manager settings. | Employing third-party tools that enhance screen management. |
| macOS | Utilizing the macOS display settings to configure the Task Manager’s position on the screen. | Using keyboard shortcuts to relocate the Task Manager window. | Employing a screen-management utility for greater control. |
| Linux | Employing window-management tools (like `xdotool`) to manipulate the Task Manager’s position. | Leveraging the desktop environment’s window-positioning features. | Using a tiling window manager for precise placement. |
Detailed Procedures for Each OS
To provide a comprehensive understanding, detailed procedures for each operating system are Artikeld below.
- Windows: The Task Manager window can be moved by simply dragging it to the desired screen. For finer control, explore the “Move to Screen” option in the Task Manager’s settings. This option may be hidden in a more advanced or specialized settings section. Some third-party screen management tools offer additional relocation features and options, but these vary in complexity.
- macOS: Adjusting the Task Manager’s screen placement in macOS is achieved through the display settings. These settings often allow for specific configurations. Keyboard shortcuts, such as `⌘ + ⌃ + ←` or `⌘ + ⌃ + →`, can also be used for relocating the Task Manager to different screens. The functionality of these shortcuts is dependent on the current configuration and preferences.
- Linux: Relocating the Task Manager on Linux often involves employing window-management tools. These tools, like `xdotool`, provide greater precision and customization in positioning the Task Manager. The methods available are highly dependent on the specific desktop environment being used. If using a tiling window manager, the relocation process may involve rearranging windows and adjusting configurations within the tiling manager.
Beneficial Relocation Scenarios
Relocating the Task Manager can significantly enhance your workflow in various scenarios. These scenarios are Artikeld below.
| Scenario | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Working with multiple applications on different screens | Allows for easy access to relevant applications and information across screens. |
| Facilitating a balanced workspace layout | Improves organization and reduces visual clutter. |
| Enhanced multitasking efficiency | Streamlines access to applications needed for different tasks. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Occasional problems may arise when relocating the Task Manager. These issues, and their solutions, are detailed below.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Task Manager not moving to the desired screen. | Ensure that the correct screen is selected in the operating system’s settings. |
| Difficulty in finding the “Move to Screen” option. | Refer to the operating system’s documentation for the specific procedure. |
| Task Manager behaving unexpectedly after relocation. | Restart the Task Manager or the operating system to resolve the issue. |
Illustrative Examples and Scenarios
Unlocking the true potential of your Task Manager often hinges on strategic placement. Moving it to the optimal screen can transform your workflow, boosting efficiency and minimizing distractions. Imagine effortlessly switching between tasks, all within a glance. This section dives deep into practical examples, showcasing how relocation and customization can enhance your overall productivity.
Scenario: The Streamlined Workflow
Relocating the Task Manager to a secondary monitor, ideally one dedicated to secondary functions or visual aids, improves workflow significantly. A designer, for instance, might place the Task Manager on a second monitor displaying reference images and color palettes. This setup allows the designer to seamlessly switch between project details, design elements, and the Task Manager, minimizing context switching and maximizing focus.
This fosters a more streamlined workflow, reducing the time wasted on shifting between screens and the associated cognitive load.
Task Manager Customization for Different Needs
Customization options allow tailoring the Task Manager to fit specific needs. A project manager might customize the Task Manager’s columns to include specific project details (e.g., deadlines, assigned personnel, progress bars). A software developer, on the other hand, might prioritize columns showing open bugs, code commits, and relevant documentation. These tailored views help users stay focused on the elements most crucial to their tasks.
The versatility of customization ensures the Task Manager remains a powerful tool, not a generic interface.
Critical Task Manager Location
In some situations, the location of the Task Manager is crucial. Consider a data analyst working on a complex financial model. Keeping the Task Manager visible, alongside the data visualizations, allows quick access to crucial information like calculations, formulas, and the ability to reference specific rows or columns without losing the overall context of the project. This close proximity facilitates instant access to critical information, eliminating the need to switch between screens, thus maintaining the analytical workflow.
This is critical for tasks requiring frequent referencing and validation.
Customizing Task Manager Appearance
The Task Manager’s appearance can be customized to suit individual preferences. A user might choose a dark theme for better readability in low-light environments, or use a specific color scheme to align with the company branding. Furthermore, users can modify the font size and style for enhanced readability. Customizable themes and settings allow for the Task Manager to be seamlessly integrated into the user’s overall aesthetic and workflow.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, relocating the task manager is a customizable process, greatly influenced by the operating system. By understanding the different methods and configurations, users can tailor their workspace to maximize efficiency and minimize distractions. The steps Artikeld in this guide offer a practical approach for achieving this, with detailed explanations and illustrations.
Clarifying Questions
Q: How can I prevent the task manager from reverting to its default screen after moving it?
A: Refer to the “Advanced Configurations and Customization” section of the guide for instructions on adjusting settings to maintain the new screen location.
Q: What are some common issues encountered when relocating the task manager?
A: Common issues include the task manager not moving, or disappearing. Detailed troubleshooting steps for various operating systems are provided in the “Troubleshooting Common Issues” section.
Q: Are there any potential conflicts between the task manager and other applications when relocating it?
A: Yes, potential conflicts may arise. The “Advanced Configurations and Customization” section addresses these possible conflicts and offers solutions.
Q: Is there a way to automate the task manager relocation process?
A: The “Advanced Configurations and Customization” section discusses possible automation options, but specifics depend on the operating system and the chosen method.
