How to see pa_expected gantt charts is crucial for project management. These visual timelines, packed with project tasks and deadlines, reveal a project’s expected progress. Understanding how to read these charts empowers you to track milestones, identify potential delays, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the process of interpreting pa_expected gantt charts, from understanding their components to using them for effective project communication and management. You’ll learn how to leverage these charts to ensure projects stay on track and meet objectives.
Understanding PA Expected Gantt Charts
A PA Expected Gantt chart is a powerful tool in project management, providing a visual representation of planned project timelines and tasks. It helps project managers and stakeholders visualize project schedules, dependencies, and potential delays. By understanding the expected durations for each activity, and how they interconnect, teams can effectively manage resources, track progress, and anticipate potential risks.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of PA Expected Gantt charts, equipping you with the knowledge to leverage their full potential.
Definition of a PA Expected Gantt Chart
A PA Expected Gantt chart is a project management tool that visually depicts the schedule of tasks in a project. It displays the start and end dates of each task, the assigned resources, and their interdependencies. Critically, it highlights the expected durations of tasks, allowing for proactive risk management. This structured approach fosters a clear understanding of the project’s timeline, making adjustments and modifications easier.
Purpose and Key Uses
The primary purpose of a PA Expected Gantt chart is to provide a clear and concise overview of the project’s schedule. It aids in planning, resource allocation, and risk assessment. Key uses include: visualizing project timelines, identifying task dependencies, estimating project duration, and monitoring progress against the expected schedule. This visual representation facilitates better communication and collaboration among project team members.
Components and Elements
A typical PA Expected Gantt chart comprises several key elements:
- Task List: A comprehensive list of all tasks involved in the project. Each task is assigned a unique identifier for easy tracking.
- Timeline: A horizontal axis representing the project timeline, typically spanning from the project start date to the completion date. This visual representation facilitates a quick understanding of the overall project duration.
- Task Bars: Rectangular bars representing individual tasks. The length of each bar corresponds to the expected duration of the task. This allows for a direct visual comparison of task durations.
- Dependencies: Arrows or lines connecting tasks to show their dependencies. This clearly demonstrates which tasks must be completed before others can begin.
- Milestones: Significant points or events within the project, often marked with symbols or labels. These milestones help monitor progress and identify key decision points.
Types of PA Expected Gantt Charts
Different project phases can benefit from tailored PA Expected Gantt charts.
- Project Initiation: This chart focuses on defining the project scope, identifying initial tasks, and establishing a preliminary timeline. This phase ensures all stakeholders have a common understanding of the project’s scope and goals.
- Project Planning: A detailed PA Expected Gantt chart is created, outlining all tasks, their durations, and dependencies. This detailed representation helps in resource allocation and risk assessment.
- Project Execution: This chart helps monitor progress against the planned schedule. Any deviations from the expected timeline are readily apparent, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments.
Visual Representation
Imagine a horizontal timeline stretching across a page. Rectangular bars, each representing a specific task, are placed along this timeline. The length of each bar corresponds to the estimated duration of the task. Connecting lines or arrows show the dependency relationships between tasks. Symbols or labels mark key milestones, allowing for a quick visual understanding of the project’s progress.
Benefits of Using PA Expected Gantt Charts
- Improved Planning: PA Expected Gantt charts facilitate better planning by providing a clear and comprehensive view of the project timeline.
- Enhanced Communication: The visual representation enhances communication among team members and stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding project timelines and tasks.
- Effective Resource Allocation: The chart aids in resource allocation by clearly showing the tasks requiring specific resources and their durations.
- Proactive Risk Management: Potential delays or bottlenecks are readily apparent, allowing for proactive risk mitigation strategies.
- Increased Transparency: The visual nature of the chart enhances transparency, making project progress readily visible to all stakeholders.
Project Management Software Support
| Software Name | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Project | Comprehensive Gantt chart capabilities, resource management, and reporting tools. | Widely used, robust features, integrates with other Microsoft products. | Can be complex to learn, may require a significant investment. |
| Asana | Simple to use Gantt chart features, collaborative project management. | Intuitive interface, easy to share and collaborate. | Limited features compared to dedicated project management software. |
| Jira | Gantt chart functionality within the issue tracking system. | Well-integrated with agile methodologies, good for tracking progress. | Might not be ideal for complex projects requiring detailed Gantt charts. |
| Monday.com | Customizable Gantt chart views, integration with various tools. | Versatile, customizable views, integrates with various apps. | Learning curve for advanced features, potential for complexity in large projects. |
Interpreting PA Expected Gantt Data
Unlock the power of your project plans with a deep dive into interpreting PA Expected Gantt charts. These visual representations of project timelines are crucial for effective project management. By understanding the tasks, dependencies, and potential risks, you can proactively manage your projects and ensure successful delivery. This guide provides practical techniques for interpreting and leveraging PA Expected Gantt charts to optimize project outcomes.
Task and Dependency Interpretation
PA Expected Gantt charts depict project tasks as bars, with their durations and start/end dates clearly visualized. Dependencies between tasks are indicated by connecting lines, showing the sequential order required for project completion. Understanding these connections is vital. For instance, a task marked as dependent on another task cannot begin until the preceding task is finished. This dependency information is critical for identifying potential bottlenecks and scheduling conflicts.
By identifying the relationships between tasks, project managers can adjust schedules and resources accordingly, maintaining project alignment.
Identifying Potential Delays and Risks
The chart’s visual nature makes identifying potential delays and risks straightforward. Tasks with short durations and numerous dependencies are often potential risk points. If a critical task is significantly delayed, it can cascade through the entire project schedule. By scrutinizing the chart for tight deadlines, overlapping tasks, and dependencies on external factors, project managers can anticipate potential issues and develop mitigation strategies.
For example, a task dependent on a supplier’s delivery could be identified as a risk and appropriate contingency plans should be established.
Estimating Task Duration
Accurate task duration estimations are fundamental for project success. The chart itself can be a useful tool. Historical data, if available, should be incorporated. For instance, similar tasks in past projects can provide valuable benchmarks for estimating the duration of current tasks. Moreover, if a task involves multiple sub-tasks, the duration of each should be estimated individually and aggregated to determine the overall duration.
Experienced project team members can provide valuable input based on their understanding of the task’s complexity and resources required.
Determining the Critical Path
The critical path is the sequence of tasks that, if delayed, directly impact the overall project completion time. It’s the longest path through the project network. Identifying this critical path allows for focused attention on tasks that have the highest impact on the project schedule. Project managers can proactively manage resources and schedule these critical tasks to minimize potential delays and maintain the project timeline.
Measuring Project Progress
Monitoring project progress against the PA Expected Gantt chart is a crucial aspect of project management. The chart’s visual representation allows for a straightforward comparison between the planned schedule and the actual progress. Tracking the completion status of tasks and updating the chart regularly allows for early identification of any deviations from the plan. This early detection allows for proactive intervention to address potential issues before they escalate.
Resource Tracking and Management
Resource allocation and management are crucial for successful project execution. The chart can be used to track resource allocation for each task, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of resource utilization. By identifying resource bottlenecks, project managers can adjust resource allocation and optimize workflow to ensure timely completion of tasks. This proactive approach to resource management prevents potential conflicts and project delays.
Visualizing Project Timelines
Different visualization techniques can be applied to PA Expected Gantt charts. Variations in chart design, such as bar color coding or task grouping, can highlight specific project aspects. Visualizations can also be customized to present the project from different perspectives, providing a more holistic view of the project’s progress. Choosing the appropriate visualization technique depends on the specific project requirements and the intended audience.
Common Symbols and Notations in PA Expected Gantt Charts
| Symbol | Description | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Bar | Represents a project task | [█] | Indicates a task’s duration and scheduled time. |
| Connecting Line | Indicates task dependencies | [─┬─] | Shows the order in which tasks must be completed. |
| Colored Bar | Highlights specific tasks or phases | [█red] | Used for emphasis, such as critical path tasks. |
| Dashed Line | Represents a potential delay | [─┼─] | Signals a risk or a possible schedule adjustment. |
Creating PA Expected Gantt Charts
Mastering the art of creating precise PA Expected Gantt charts is crucial for project success. These charts visually represent project timelines, task dependencies, and resource allocation, allowing for proactive management and efficient execution. This detailed guide will equip you with the necessary skills to construct effective charts, ensuring accurate estimations and optimal resource utilization.
Steps Involved in Chart Creation
Creating a PA Expected Gantt chart involves several key steps. First, meticulously define each task within the project, outlining its specific deliverables. Next, estimate the duration for each task, considering potential complexities and dependencies. Subsequently, establish the sequence of tasks, identifying and documenting any prerequisites or subsequent steps. Finally, visualize these tasks and dependencies on a timeline, allocating resources to each task as appropriate.
This systematic approach ensures a comprehensive and accurate representation of the project’s expected timeline.
Incorporating Task Dependencies
Task dependencies are crucial elements in a Gantt chart. They illustrate the sequential nature of tasks, where one task cannot begin until another is completed. For example, a software development project might have a “Design UI” task that must precede the “Develop Front-End” task. Visualizing these dependencies on the chart is accomplished by connecting the tasks with arrows.
The “Design UI” task’s end date will determine when the “Develop Front-End” task can begin. This ensures the project progresses in a logical and predictable manner.
Best Practices for Clear and Effective Charts
To ensure a clear and effective Gantt chart, adhere to these best practices: use a consistent timescale, clearly label tasks, and use distinct colors to represent different phases or team members. Detailed task descriptions help clarify expectations and avoid misinterpretations. Regular updates and revisions are essential for maintaining chart accuracy as the project evolves.
Estimating Task Durations Accurately
Accurate task duration estimation is critical for project planning. Utilize historical data from similar projects, gather input from experienced team members, and consider potential risks or uncertainties. For instance, if a task involves a new technology, allocate a buffer to account for unforeseen delays. Consider employing statistical techniques, such as the Beta distribution, for more nuanced estimations, leading to a more precise and reliable timeline.
Managing Resources Effectively
Resource management is vital for a successful project. Clearly identify the resources required for each task, such as personnel, equipment, or materials. Track resource availability and allocate them accordingly to avoid bottlenecks or conflicts. For example, if two tasks require the same specialized engineer, scheduling conflicts must be addressed to prevent delays. Effective resource management ensures smooth project execution.
Tools and Software for Chart Creation
Numerous tools and software are available for creating Gantt charts. Popular choices include Microsoft Project, GanttProject, and various online project management platforms. These tools offer features for task creation, dependency mapping, resource allocation, and visualization. Selecting the appropriate tool depends on the project’s scope and the team’s familiarity with specific software.
Chart Views Available
| View Name | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gantt Chart View | Displays tasks as bars on a timeline, showing dependencies and durations. | Excellent for visualizing project timeline, dependencies, and progress. | Can become cluttered for complex projects. |
| Resource Allocation View | Highlights the allocation of resources (personnel, equipment) across tasks. | Effective for resource planning and identifying potential bottlenecks. | May not be as comprehensive for visualizing project timelines. |
| Task Breakdown Structure (TBS) View | Hierarchical view showing tasks and subtasks within a project. | Useful for organizing and managing complex projects with many tasks. | May not be as intuitive for understanding the overall project timeline. |
| Calendar View | Displays tasks on a calendar grid, providing a day-by-day overview of project activities. | Excellent for scheduling meetings and tracking daily tasks. | Can obscure dependencies and overall project progress. |
Using PA Expected Gantt Charts for Project Management: How To See Pa_expected Gantt
PA Expected Gantt charts are powerful tools for visualizing project timelines and resources. This section details how to leverage these charts effectively for project management, from stakeholder communication to risk mitigation and resource optimization. Mastering these techniques will significantly improve project success rates.Effective project management relies on clear communication and proactive risk management. A well-utilized PA Expected Gantt chart facilitates both, providing a single, comprehensive view of the project’s scope, timeline, and resources.
This empowers stakeholders and project managers to make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
Communicating Project Timelines to Stakeholders
Utilizing a PA Expected Gantt chart for stakeholder communication involves presenting a clear, visual representation of the project timeline. This enables stakeholders to understand the project’s scope, critical milestones, and overall duration at a glance. The visual nature of the chart aids comprehension, making it an effective tool for conveying complex information. Highlighting key milestones and dependencies can further enhance understanding.
Specific tasks and their estimated durations are readily apparent, fostering a shared understanding of project expectations.
Managing Project Budgets with PA Expected Gantt Charts, How to see pa_expected gantt
PA Expected Gantt charts can assist in managing project budgets by linking task durations with resource costs. Project managers can allocate resources to specific tasks based on their duration and associated costs, facilitating informed budgeting decisions. By visualizing task dependencies and estimated durations, potential budget overruns can be identified early on, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies. The chart facilitates tracking actual costs against planned costs, ensuring financial accountability.
For example, if a task takes longer than anticipated, the associated budget can be adjusted accordingly.
Incorporating Project Changes into PA Expected Gantt Charts
Project changes are inevitable. A PA Expected Gantt chart provides a flexible framework for incorporating these modifications. By updating task durations, dependencies, and milestones, the chart reflects the altered project plan. This visual representation of changes allows stakeholders to understand the impact of modifications on the overall project timeline. The chart facilitates the re-estimation of resources and time, enabling project managers to accurately assess the impact of changes on the budget and overall project timeline.
For instance, if a new task is added, its duration and dependencies can be included in the chart.
Identifying and Mitigating Potential Risks
A PA Expected Gantt chart is useful for identifying potential risks. By highlighting potential bottlenecks and dependencies, the chart allows for proactive risk mitigation. Project managers can identify tasks with high risk potential, then plan mitigation strategies. The chart’s visual representation helps in identifying potential delays or resource constraints. For example, if a task has a critical path and a high risk of delay, the chart will immediately highlight it.
Tracking Project Milestones with PA Expected Gantt Charts
PA Expected Gantt charts effectively track project milestones. Milestones are significant events marking completion of specific project phases. By visually representing these milestones, project progress can be easily monitored. The chart enables project managers to compare the actual progress against the planned milestones, identifying any deviations early on. Visualizing milestones aids in tracking and communicating progress to stakeholders, ensuring alignment with project goals.
For instance, if a milestone is delayed, the chart highlights this deviation, prompting a prompt response.
Optimizing Resource Allocation with PA Expected Gantt Charts
PA Expected Gantt charts facilitate optimized resource allocation. By visualizing task dependencies and resource requirements, project managers can effectively allocate resources to specific tasks. This optimized resource allocation minimizes idle time and enhances productivity. The chart enables efficient allocation of personnel, materials, and other resources, leading to improved project outcomes. For instance, if a task requires a specific skill set, the chart can help in identifying the right resource.
Best Practices for Effectively Using PA Expected Gantt Charts in Project Management
- Regularly update the chart to reflect project progress and changes.
- Ensure accurate estimations of task durations and resource requirements.
- Involve stakeholders in the creation and review of the chart.
- Utilize the chart for proactive risk management and mitigation.
- Use the chart to communicate project progress and timelines to stakeholders.
Accurate estimations are crucial for effective project management. Realistic estimations, including potential delays or resource constraints, are key to effective project management. Stakeholder input is essential for the accuracy of the chart, ensuring that all project requirements are accounted for. By regularly updating the chart, project managers can monitor progress and identify potential issues. The chart serves as a visual representation of the project plan, enabling proactive risk management and mitigation.
Common Project Communication Strategies Leveraging PA Expected Gantt Charts
| Communication Strategy | Description | Example | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Presentation | Using the chart to display project timelines and progress to stakeholders. | Presenting the Gantt chart during a stakeholder meeting. | Pros: Clear and concise; Cons: Can be overwhelming if not presented effectively. |
| Regular Updates | Providing regular updates on project progress using the chart. | Sending weekly updates highlighting progress on the Gantt chart. | Pros: Keeps stakeholders informed; Cons: Requires consistent effort. |
| Interactive Workshops | Using the chart as a basis for collaborative discussions with stakeholders. | Holding workshops where stakeholders can provide feedback on the Gantt chart. | Pros: Fosters engagement; Cons: Can be time-consuming. |
| Milestone Reporting | Communicating project progress based on milestones tracked on the chart. | Sending progress reports highlighting achievement of specific milestones. | Pros: Straightforward; Cons: May not provide a complete picture. |
Advanced PA Expected Gantt Chart Techniques
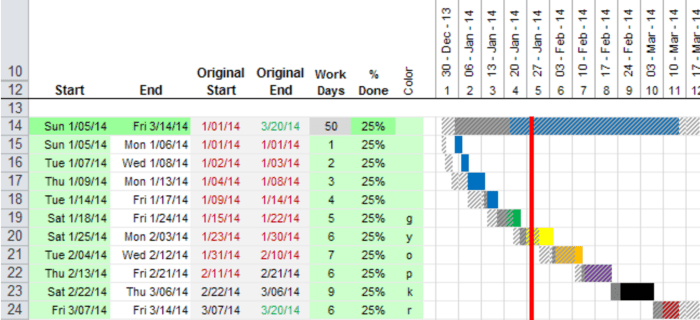
Unlock the full potential of your project plans with advanced PA Expected Gantt chart techniques. Mastering these methods allows you to visualize complex projects with unparalleled clarity, enabling more accurate estimations and efficient resource allocation. This section delves into strategies for creating more intricate charts, incorporating external data, and visualizing dependencies, ultimately boosting project success.Leveraging advanced techniques empowers project managers to make informed decisions.
By mastering conditional formatting, different chart types, and interactive elements, you gain a deeper understanding of your project’s progress and potential challenges. This detailed guide will equip you with the tools necessary to craft insightful PA Expected Gantt charts, leading to more successful project outcomes.
Conditional Formatting for Enhanced Insights
Conditional formatting allows you to highlight specific information within the Gantt chart. This feature is crucial for quickly identifying critical paths, potential delays, or areas requiring immediate attention. By assigning specific colors or styles to tasks based on criteria like deadlines, budget overruns, or resource constraints, you instantly pinpoint areas that need focused management. For example, tasks exceeding their planned duration could be highlighted in red, while tasks completed ahead of schedule might be displayed in green.
Utilizing Diverse Chart Types for Comprehensive Views
Beyond the standard bar chart, explore alternative chart types to cater to different project needs. A combination of bar charts, network diagrams, and even Kanban boards can offer a more holistic view of the project’s progression. A network diagram can effectively display complex dependencies between tasks, while a Kanban board provides a dynamic visualization of workflow. For example, when dealing with a project with numerous interconnected subtasks, a network diagram can reveal potential bottlenecks and dependencies, facilitating a more comprehensive view than a traditional Gantt chart alone.
Integrating External Data for Informed Decisions
Integrating external data sources enriches the PA Expected Gantt chart. This includes pulling in data from financial systems, resource allocation tools, or even weather forecasts (for outdoor projects). This enables a more realistic and detailed projection of project timelines and costs. For instance, incorporating weather data into a construction project Gantt chart allows for proactive adjustments to potential delays.
By linking the Gantt chart to real-world factors, you create a more robust and adaptable project plan.
Visualizing Project Dependencies in Complex Projects
Complex projects often involve intricate dependencies between tasks. Gantt charts can visualize these dependencies through linked tasks and critical path analysis. Using these methods, you can effectively identify the tasks most crucial to the overall project timeline. If task A must be completed before task B, you can create a visual link between the two, highlighting the sequence of activities.
This helps project managers anticipate potential delays and adapt plans accordingly.
Interactive Gantt Charts for Dynamic Management
Interactive Gantt charts provide real-time updates and allow users to manipulate the schedule directly. This enhances flexibility and allows for more agile project management. For example, a project manager can easily drag and drop tasks to adjust timelines, simulate different scenarios, or dynamically respond to unexpected events. Interactive features also allow for a more user-friendly and engaging experience for stakeholders involved in the project.
Visual Cues for Enhanced Readability
Employing visual cues, like different colors, shapes, or sizes, can significantly improve the readability and comprehension of PA Expected Gantt charts. This enhances the effectiveness of the visual representation, making it easier to interpret project progress. For instance, tasks assigned to specific resources can be highlighted with distinct colors. A task’s priority level could be reflected by font size or symbol.
Comparing Different Gantt Chart Visualizations
| Chart Type | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bar Chart | Standard Gantt chart representation | Easy to understand, widely used | Limited for complex projects |
| Network Diagram | Visualizes task dependencies | Excellent for complex projects, identifies critical paths | Can be overwhelming for simple projects |
| Kanban Board | Visual representation of workflow | Great for dynamic projects, easy to update | Less effective for showing timelines |
| Calendar View | Shows project timeline on a calendar | Easy to understand project scheduling in relation to dates | Limited in depicting task dependencies |
Final Conclusion

In conclusion, mastering how to see pa_expected gantt charts is a key skill for effective project management. By understanding the charts’ components, interpreting the data, and applying advanced techniques, you can gain valuable insights into project timelines, risks, and resource allocation. This guide provides a practical approach to utilizing these powerful tools, equipping you with the knowledge to succeed in your projects.
FAQ
What software can I use to view PA_Expected Gantt charts?
Many project management software packages support Gantt charts. Examples include Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, and Jira. Specific features may vary.
How do I identify critical tasks in a PA_Expected Gantt chart?
Critical tasks are those on the critical path, which is the longest sequence of tasks that determine the overall project duration. Look for tasks with no slack or float.
What are some common symbols used in PA_Expected Gantt charts?
Common symbols include bars to represent tasks, dependencies to illustrate relationships between tasks, and milestones for key project events. Check the specific software for precise symbols.
How do I interpret task dependencies in a PA_Expected Gantt chart?
Dependencies indicate which tasks must be completed before others can begin. Arrows or lines between tasks show these relationships, enabling you to visualize the project’s sequential flow.
